UNIT 7. ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION A. VOCABULARY WORD PRONNCIATION MEANING carbon dioxide (n) /ˌkɑːrbən daɪˈɒksaɪd/ khí cacbonic/ cacbon đioxit
E.g. Trees absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen. Cây xanh hấp thụ khí cacbonic và tạo ra khí oxi. carbon footprint (n) /ˌkɑːrbən ˈfʊtprɪnt/ dấu chân cacbon
(tổng lượng phát thải khí nhà kính)
E.g. We need to reduce our carbon footprint. Chúng ta cần giảm bớt dấu chân cacbon của mình. coral (n) /ˈkɒrəl/ san hô
E.g. She was wearing a coral necklace. Cô ấy đang đeo một chiếc vòng cổ bằng san hô. dugong (n) /ˈduːɡɒŋ/ con cá cúi, bò biển
E.g. The fisherman found a rare dugong in the water. Ngư dân tìm thấy một con bò biển quý hiếm dưới nước. ecosystem (n) /ˈiːkəʊsɪstəm/ hệ sinh thái
E.g. This bay has a very complex ecosystem. Vịnh này có một hệ sinh thái rất phức tạp.
endangered species (n) /ɪnˈdeɪndʒəd ˈspiːʃiːz /
các loài động thực vật có nguy cơ bị tuyệt chủng
E.g. Mountain gorillas are an endangered species. Khỉ đột núi là một loài có nguy cơ tuyệt chủng. extinction (n) /ɪkˈstɪŋkʃn/
sự tuyệt chủng, tuyệt diệt
E.g. Pandas are on the margin of extinction. Gấu trúc đang trên bờ vực tuyệt chủng. habitat (n) /ˈhæbɪtæt/ môi trường sống
E.g. This type of owl prefers a desert habitat. Loại cú này thích môi trường sống sa mạc. oxygen (n) /ˈɒksɪdʒən/ khí ô-xi
E.g. Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. Hydro và oxy kết hợp để tạo thành nước. participate (n) /pɑːrˈtɪsɪpeɪt/ tham gia
E.g. I hope everyone will participate in this discussion. Tôi hy vọng mọi người sẽ tham gia vào cuộc thảo luận này. product (n) /ˈprɒdʌkt/ sản phẩm
E.g. They put a new product on the market. Họ đưa một sản phẩm mới ra thị trường. protect (n) /prəˈtekt/ bảo vệ
E.g. We should protect the environment. Chúng ta nên bảo vệ môi trường. release (n) /rɪˈliːs/ thải ra, làm thoá Giao t a ra
nde thitienganh.info sưu tầm
E.g. Coal power stations release sulfur dioxide into the air. Các nhà máy điện than giải phóng lưu
huỳnh đi-ô-xít vào không khí. resident (n) /ˈrezɪdənt/ người dân, dân cư
E.g. She’s a resident here. Cô ấy là một cư dân ở đây. single-use (n) /ˌsɪŋɡl ˈjuːs/ để sử dụng một lần
E.g. Sales of single-use cameras fell by 2% last year. Doanh số bán máy ảnh dùng một lần đã giảm 2% trong năm ngoái. species (n) /ˈspiːʃiːz/
giống, loài động thực vật
E.g. Many species disappeared during the Ice Age. Nhiều loài đã biến mất trong Kỷ băng hà. substance (n) /ˈsʌbstəns/ chất
E.g. Some frogs produce toxic substances in their skin. Một số loài ếch sản sinh ra các chất độc hại trong da của chúng toxic (n) /ˈtɒksɪk/ độc hại
E.g. Many pesticides are highly toxic. Nhiều loại thuốc trừ sâu có độc tính cao. B. WORD FORMATION Word Related words Transcription Meaning endangered (adj) /ɪnˈdeɪndʒəd/
trong tình trạng bị đe doạ endanger(v) /ɪnˈdeɪndʒər/ gây nguy hiểm endangerment (n) /ɪnˈdeɪndʒərmənt/ tình trạng bị đe doạ endangerer (n) /ɪnˈdeɪndʒərər/
người hoặc vật gây ra mối đe doạ endangering (adj) /ɪnˈdeɪndʒərɪŋ/ tình trạng bị de dọa extinction (n) /ɪkˈstɪŋkʃn/
sự tuyệt chủng, tuyệt diệt extinct (adj) /ɪkˈstɪŋkt/ tuyệt chủng habitat (n) /ˈhæbɪtæt/ môi trường sống habitable (adj) /ˈhæbɪtəbl/ có thể sống được habitation (n) /ˌhæbɪˈteɪʃn/ sự cư trú, nơi cư trú inhabitant (n) /ɪnˈhæbɪtənt cư dân, người cư ngụ product (n) /ˈprɒdʌkt/ sản phẩm production (n) /prəˈdʌkʃn/ sự sản xuất produce (n) /prəˈdjuːs/ sản lượng produce (v) /prəˈdjuːs/ sản xuất, chế tạo producer (n) /prəˈduːsər/ nhà sản xuất protect (v) /prəˈtekt/ bảo vệ protection (n) /prəˈtekʃn/ sự bảo vệ toxic (adj) /ˈtɒksɪk/ độc hại non-toxic (adj) /ˌnɒn ˈtɒksɪk không độc hại toxicity (n) /tɒkˈsɪsəti/ độc tố, độc tính C. GRAMMAR
Complex sentences with adverb clauses of time (Câu phức với mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian) 1. Complex sentences
- Câu phức là câu bao gồm 1 mệnh đề độc lập (independent clause) và ít nhất 1 mệnh đề phụ thuộc
(dependent clause) liên kết với nhau. Hai mệnh đề thường được nối với nhau bởi dấu phẩy hoặc các
liên từ phụ thuộc (subordinating conjunctions).
E.g. My father always takes time to play with me even though he is very busy. Mệnh đề độc lập Mệnh đề phụ thuộc
(Bố của tôi luôn dành thời gian để chơi với tôi mặc dù ông rất bận rộn.) Hoặc:
Even though my father is very busy, he always takes time to play with me.
Mệnh đề phụ thuộc Mệnh đề độc lập
(Mặc dù bố tôi rất bận rộn, nhưng ông luôn dành thời gian để chơi với tôi.)
- Trong câu phức, chúng ta thường gặp một số dạng mệnh đề phụ thuộc phổ biến sau: mệnh đề trạng
ngữ chỉ nguyên nhân lý do (adverb clause of reason), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian (adverb clause
of time), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ sự nhượng bộ (adverb clause of concession), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ
mục đích (adverb clause of purpose), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ kết quả (adverb clause of results).
2. Adverb clauses of time (Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian) 2.1. Định nghĩa
Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian là những mệnh đề bắt đầu bằng các liên từ chỉ thời gian như: when
(khi, vào lúc), while, as (trong khi), until, till (cho đến khi), as soon as, once (ngay khi), before, by the
time (trước khi), after (sau khi), as long as, so long as (chừng nào mà), since (từ khi)... E.g.
I hope to pay him a visit before I go away.
(Tôi hy vọng đến thăm được anh ấy trước khi tôi đi.)
When we were in New York, we saw several plays.
(Khi chúng tôi ở New York, chúng tôi đã xem một vài vở kịch.)
As soon as you are ready, we shall go.
(Ngay khi cậu sẵn sàng, chúng ta sẽ đi.)
We stayed there until it stopped raining.
(Chúng tôi đã ở đó cho đến khi trời ngừng mưa.)
- Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian có thể đứng đầu hoặc cuối câu. Nếu mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời
gian đứng ở đầu câu sẽ ngăn cách với mệnh đề chính bằng dấu phẩy. 2.2. Cách sử dụng
a. Diễn đạt 1 hành động đang xảy ra thì hành động khác xen vào Main clause Conjunction Adverb clause of time S + V-ed while S+ was/ were + V-ing (quá khứ đơn) as
(quá khứ tiếp diễn) S + was/ were + V-ing when S + V-ed
(quá khứ tiếp diễn) (quá khứ đơn) E.g.
We were having dinner when she came.
(Khi cô ấy tới, chúng tôi đang ăn tối.)
As I was walking home, it began to rain.
(Khi chúng tôi đang đi bộ về nhà thì trời bắt đầu mưa.)
b. Diễn tả hai hành động diễn ra song song Main clause Conjunction Adverb clause of time S+ is/am/are +V-ing while S+ is/am/are +V-ing S + was/ were +V-ing S + was/ were +V-ing
Bài tập bổ trợ nâng cao Tiếng Anh lớp 8 Global success Kì 2
7.3 K
3.6 K lượt tải
MUA NGAY ĐỂ XEM TOÀN BỘ TÀI LIỆU
CÁCH MUA:
- B1: Gửi phí vào TK:
1133836868- CT TNHH DAU TU VA DV GD VIETJACK - Ngân hàng MB (QR) - B2: Nhắn tin tới Zalo VietJack Official ( nhấn vào đây ) để xác nhận thanh toán và tải tài liệu - giáo án
Liên hệ ngay Hotline hỗ trợ: 084 283 45 85
Tài liệu được cập nhật liên tục trong gói này từ nay đến hết tháng 3/2024. Chúng tôi đảm bảo đủ số lượng đề đã cam kết hoặc có thể nhiều hơn, tất cả có BẢN WORD, LỜI GIẢI CHI TIẾT và tải về dễ dàng.
Để tải tài liệu gốc về máy bạn click vào nút Tải Xuống ở trên!
Bộ tài liệu bao gồm: 6 tài liệu lẻ (mua theo bộ tiết kiệm đến 50%)
Thuộc bộ (mua theo bộ để tiết kiệm hơn):
- Tailieugiaovien.com.vn giới thiệu Bài tập bổ trợ nâng cao Tiếng Anh 8 Global success Kì 2 mới nhất nhằm giúp Giáo viên có thêm tài liệu tham khảo bài tập Tiếng Anh 8.
- File word có lời giải chi tiết 100%.
- Mua trọn bộ sẽ tiết kiệm hơn tải lẻ 50%.
Đánh giá
4.6 / 5(7250 )5
4
3
2
1
Trọng Bình
Tài liệu hay
Giúp ích cho tôi rất nhiều
Duy Trần
Tài liệu chuẩn
Rất thích tài liệu bên VJ soạn (bám sát chương trình dạy)
TÀI LIỆU BỘ BÁN CHẠY MÔN Tiếng Anh
Xem thêmTÀI LIỆU BỘ BÁN CHẠY Lớp 8
Xem thêmTài liệu bộ mới nhất
UNIT 7. ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
A. VOCABULARY
WORD
PRONNCIATION
MEANING
carbon dioxide (n)
/ˌkɑːrbən daɪˈɒksaɪd/
khí cacbonic/ cacbon đioxit
E.g. Trees absorb carbon dioxide and produce oxygen. Cây xanh hấp thụ khí cacbonic và tạo ra khí
oxi.
carbon footprint (n)
/ˌkɑːrbən ˈfʊtprɪnt/
dấu chân cacbon
(tổng lượng phát thải khí nhà kính)
E.g. We need to reduce our carbon footprint. Chúng ta cần giảm bớt dấu chân cacbon của mình.
coral (n)
/ˈkɒrəl/
san hô
E.g. She was wearing a coral necklace. Cô ấy đang đeo một chiếc vòng cổ bằng san hô.
dugong (n)
/ˈduːɡɒŋ/
con cá cúi, bò biển
E.g. The sherman found a rare dugong in the water. Ngư dân m thấy một con bò biển quý hiếm
dưới nước.
ecosystem (n)
/ˈiːkəʊsɪstəm/
hệ sinh thái
E.g. This bay has a very complex ecosystem. Vịnh này có một hệ sinh thái rất phức tạp.
endangered species (n)
/ɪnˈdeɪndʒəd ˈspiːʃiːz /
các loài động thực vật có nguy cơ bị tuyệt chủng
E.g. Mountain gorillas are an endangered species. Khỉ đột núi là một loài có nguy cơ tuyệt chủng.
exncon (n)
/ɪkˈstɪŋkʃn/
sự tuyệt chủng, tuyệt diệt
E.g. Pandas are on the margin of exncon. Gấu trúc đang trên bờ vực tuyệt chủng.
habitat (n)
/ˈhæbɪtæt/
môi trường sống
E.g. This type of owl prefers a desert habitat. Loại cú này thích môi trường sống sa mạc.
oxygen (n)
/ˈɒksɪdʒən/
khí ô-xi
E.g. Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. Hydro và oxy kết hợp để tạo thành nước.
parcipate (n)
/pɑːrˈtɪsɪpeɪt/
tham gia
E.g. I hope everyone will parcipate in this discussion. Tôi hy vọng mọi người sẽ tham gia vào cuộc
thảo luận này.
product (n)
/ˈprɒdʌkt/
sản phẩm
E.g. They put a new product on the market. Họ đưa một sản phẩm mới ra thị trường.
protect (n)
/prəˈtekt/
bảo vệ
E.g. We should protect the environment. Chúng ta nên bảo vệ môi trường.
release (n)
/rɪˈliːs/
thải ra, làm thoát ra
E.g. Coal power staons release sulfur dioxide into the air. Các nhà máy điện than giải phóng lưu
huỳnh đi-ô-xít vào không khí.
resident (n)
/ˈrezɪdənt/
người dân, dân cư
E.g. She’s a resident here. Cô ấy là một cư dân ở đây.
single-use (n)
/ˌsɪŋɡl ˈjuːs/
để sử dụng một lần
E.g. Sales of single-use cameras fell by 2% last year. Doanh số bán máy ảnh dùng một lần đã giảm 2%
trong năm ngoái.
species (n)
/ˈspiːʃiːz/
giống, loài động thực vật
E.g. Many species disappeared during the Ice Age. Nhiều loài đã biến mất trong Kỷ băng hà.
substance (n)
/ˈsʌbstəns/
chất
E.g. Some frogs produce toxic substances in their skin. Một số loài ếch sản sinh ra các chất độc hại
trong da của chúng
toxic (n)
/ˈtɒksɪk/
độc hại
E.g. Many pescides are highly toxic. Nhiều loại thuốc trừ sâu có độc nh cao.
B. WORD FORMATION
Word
Related words
Transcripon
Meaning
endangered (adj)
/ɪnˈdeɪndʒəd/
trong nh trạng bị đe doạ
endanger(v)
/ɪnˈdeɪndʒər/
gây nguy hiểm
endangerment (n)
/ɪnˈdeɪndʒərmənt/
nh trạng bị đe doạ
endangerer (n)
/ɪnˈdeɪndʒərər/
người hoặc vật gây ra mối đe doạ
endangering (adj)
/ɪnˈdeɪndʒərɪŋ/
nh trạng bị de dọa
exncon (n)
/ɪkˈstɪŋkʃn/
sự tuyệt chủng, tuyệt diệt
exnct (adj)
/ɪkˈstɪŋkt/
tuyệt chủng
habitat (n)
/ˈhæbɪtæt/
môi trường sống
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm
habitable (adj)
/ˈhæbɪtəbl/
có thể sống được
habitaon (n)
/ˌhæbɪˈteɪʃn/
sự cư trú, nơi cư trú
inhabitant (n)
/ɪnˈhæbɪtənt
cư dân, người cư ngụ
product (n)
/ˈprɒdʌkt/
sản phẩm
producon (n)
/prəˈdʌkʃn/
sự sản xuất
produce (n)
/prəˈdjuːs/
sản lượng
produce (v)
/prəˈdjuːs/
sản xuất, chế tạo
producer (n)
/prəˈduːsər/
nhà sản xuất
protect (v)
/prəˈtekt/
bảo vệ
protecon (n)
/prəˈtekʃn/
sự bảo vệ
toxic (adj)
/ˈtɒksɪk/
độc hại
non-toxic (adj)
/ˌnɒn ˈtɒksɪk
không độc hại
toxicity (n)
/tɒkˈsɪsə/
độc tố, độc nh
C. GRAMMAR
Complex sentences with adverb clauses of me (Câu phức với mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian)
1. Complex sentences
- Câu phức là câu bao gồm 1 mệnh đề độc lập (independent clause) và ít nhất 1 mệnh đề phụ thuộc
(dependent clause) liên kết với nhau. Hai mệnh đề thường được nối với nhau bởi dấu phẩy hoặc các
liên từ phụ thuộc (subordinang conjuncons).
E.g. My father always takes me to play with me even though he is very busy.
Mệnh đề độc lập Mệnh đề phụ thuộc
(Bố của tôi luôn dành thời gian để chơi với tôi mặc dù ông rất bận rộn.)
Hoặc:
Even though my father is very busy, he always takes me to play with me.
Mệnh đề phụ thuộc Mệnh đề độc lập
(Mặc dù bố tôi rất bận rộn, nhưng ông luôn dành thời gian để chơi với tôi.)
- Trong câu phức, chúng ta thường gặp một số dạng mệnh đề phụ thuộc phổ biến sau: mệnh đề trạng
ngữ chỉ nguyên nhân lý do (adverb clause of reason), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian (adverb clause
of me), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ sự nhượng bộ (adverb clause of concession), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ
mục đích (adverb clause of purpose), mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ kết quả (adverb clause of results).
2. Adverb clauses of me (Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian)
2.1. Định nghĩa
Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian là những mệnh đề bắt đầu bằng các liên từ chỉ thời gian như: when
(khi, vào lúc), while, as (trong khi), unl, ll (cho đến khi), as soon as, once (ngay khi), before, by the
me (trước khi), aer (sau khi), as long as, so long as (chừng nào mà), since (từ khi)...
E.g. I hope to pay him a visit before I go away.
(Tôi hy vọng đến thăm được anh ấy trước khi tôi đi.)
When we were in New York, we saw several plays.
(Khi chúng tôi ở New York, chúng tôi đã xem một vài vở kịch.)
As soon as you are ready, we shall go.
(Ngay khi cậu sẵn sàng, chúng ta sẽ đi.)
We stayed there unl it stopped raining.
(Chúng tôi đã ở đó cho đến khi trời ngừng mưa.)
- Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian có thể đứng đầu hoặc cuối câu. Nếu mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời
gian đứng ở đầu câu sẽ ngăn cách với mệnh đề chính bằng dấu phẩy.
2.2. Cách sử dụng
a. Diễn đạt 1 hành động đang xảy ra thì hành động khác xen vào
Main clause
Conjuncon
Adverb clause of me
S + V-ed
(quá khứ đơn)
while
as
S+ was/ were + V-ing
(quá khứ ếp diễn)
S + was/ were + V-ing
(quá khứ ếp diễn)
when
S + V-ed
(quá khứ đơn)
E.g. We were having dinner when she came.
(Khi cô ấy tới, chúng tôi đang ăn tối.)
As I was walking home, it began to rain.
(Khi chúng tôi đang đi bộ về nhà thì trời bắt đầu mưa.)
b. Diễn tả hai hành động diễn ra song song
Main clause
Conjuncon
Adverb clause of me
S+ is/am/are +V-ing
S + was/ were +V-ing
while
S+ is/am/are +V-ing
S + was/ were +V-ing
(chia ở thì ếp diễn)
(chia ở thì ếp diễn)
E.g. I was cooking dinner while my husband was reading a book.
(Tôi đang nấu bữa tối trong khi chồng tôi đang đọc sách.)
She is playing tennis while her brother is listening to music.
(Trong khi cô ấy đang chơi tennis thì anh trai cô ấy lại đang nghe nhạc.)
c. Đối với hiện tại hoàn thành, sau since (từ khi) luôn chia ở thì quá khứ đơn
Main clause
Conjuncon
Adverb clause of me
S + has/ have + PII
(hiện tại hoàn thành)
since
S + Ved
(quá khứ đơn)
E.g. I haven’t met her since she le school.
(Tôi đã không gặp cô ấy từ khi cô ấy nghỉ học ở trường.)
She has played the piano since she was a child.
(Cô ấy đã chơi piano từ khi cô ấy còn nhỏ.)
d. Hành động hoàn thành trước hành động khác trong quá khứ
Main clause
Conjuncon
Adverb clause of me
S + V-ed
(quá khứ đơn)
aer
as soon as
S+ had + PII
(quá khứ hoàn thành)
S+ had + PII
(quá khứ hoàn thành)
before
by the me
S + V-ed
(quá khứ đơn)
E.g. By the me we arrived, he had already le.
(Khi chúng tôi đến, anh ấy đã rời đi rồi.)
She got a job aer she had graduated from university.
(Cô ấy đi làm sau khi đã tốt nghiệp đại học.)
e. Nối các hành động xảy ra trong tưomg lai
Main clause
Conjuncon
Adverb clause of me
S + will + V
S + be going to + V
(Tương lai đơn/ tương lai gần)
when
as soon as
aer
before
unl
S + V-s/es
S + have/has + PII
(hiện tại đơn/ hiện tại hoàn thành)

E.g. I’ll go to bed aer I have nished my homework.
(Tôi sẽ đi ngủ sau khi tôi làm xong bài tập về nhà.)
When John comes, we will give him your leer.
(Khi John đến, chúng tôi sẽ gửi cho anh ta bức thư của cậu.)
D. PRONUNCIATION
Clusters: /bl/ and /kl/
1. /bl/
/bl/ = /b/ + /l/
/b/: mím nhẹ hai môi lại và nâng phần ngạc mềm để chặn luồng hơi trong
khoang miệng, rồi mở miệng bật hơi từ phía trong ra. Khi phát âm, dây thanh
sẽ rung lên.
/l/: để đầu lưỡi chạm vào lợi của hàm răng trên. Khi phát âm, luồng hơi sẽ đi
qua khoảng trống giữa lưỡi và khoang miệng ra ngoài.
E.g.
blue
blink
black
bleed
blossom
blur
blend
blanch
2. /kl/
/kl/ = /k/ + /l/
/k/: mở miệng, cuống lưỡi co lại, chạm vào phần ngạc mềm hay là phần trong
cùng của vòm miệng để chặn luồng khí trong miệng. Sau đó bật mạnh luồng
khí ra khỏi miệng mà không làm rung dây thanh trong cổ họng.
/l/: để đầu lưỡi chạm vào lợi của hàm răng trên. Khi phát âm, luồng hơi sẽ đi
qua khoảng trống giữa lưỡi và khoang miệng ra ngoài.
E.g.

clock
bicycle
eclipse
circle
clause
classic
3. Sự khác nhau giữa /bl/ và /kl/
Về mặt âm thanh: sự khác biệt của cụm phụ âm /bl/ và /kl/ xuất phát từ sự khác biệt của vị trí môi và
lưỡi khi bật hơi phát âm âm /b/ và /k/.
- Khi phát âm âm /b/ chúng ta mím nhẹ môi, còn âm /k/ chúng ta cần mở miệng.
- Với âm /b/ các em để lưỡi thả lỏng như bình thường trong khi với âm /k/ các em co cuống lưỡi lại,
chạm vào phần ngạc mềm để chặn luồng khí trong miệng.
- Phát âm âm /b/ làm rung dây thanh trong cổ họng nhưng âm /k/ thì không.
/bl/
/kl/
blue
clue
block
clock
blink
clink
E. PRACTICE
Exercise 1. Look and put the word under the correct photo. Then pronounce it correctly.
blow
clown
classroom
blossom
cli
blanket
clean
blind
1. ________________
2. ________________
3. ________________
4. ________________
5. ________________
6. ________________
7. ________________
8. ________________
Exercise 2. Use single underline with the word containing /bl/ and double underline with the word
containing /kl/. Then read the sentences aloud (pay aenon to the sound /bl/ and /kl/).
1. He wore a navy blue blazer to the wedding.
2. I need to clean my room before my parents come home.
3. The blizzard covered the enre town with snow.
4. The audience started to clap when the musician nished playing.
5. She covered herself with a warm blanket in a cold winter night.
6. The cut on his hand was deep and started to bleed.
7. The water in the lake is so clear that you can see the sh swimming.
8. Don’t blame me for your mistakes.
9. The tropical climate in this region is hot and humid.
10. Sarah is in the 5
th
grade class at her school.
Exercise 3. Complete the sentences with the words in the box.
staons
endangered
carbon
exncon
environment
combine
ecosystem
sherman
absorb
parcipate
1. Pandas are on the margin of ________________.
2. The ________________found a rare dugong in the water.
3. I hope everyone will ________________in this discussion.
4. We should protect the ________________.
5. Coal power ________________release sulfur dioxide into the surrounding air.
6. Hydrogen and oxygen ________________to form water.
7. Trees ________________carbon dioxide and produce oxygen.
8. We need to reduce our ________________footprint.
9. This bay has a very complex ________________.
10. Mountain gorillas are an ________________species.
Exercise 4. Put each type of polluon with its descripon.
noise polluon
radioacve polluon
water polluon
visual polluon
thermal polluon
light polluon
soil polluon
air polluon
Descripon
Type of polluon
1. Too much use of electric lights
2. Caused by the smoke and harmful gases from vehicles and factories.
3. The noise which is harmful to humans and animals. This includes the
sound of vehicles, loud speakers...
4. Telephone towers, power lines, adversing billboards obstruct
people from enjoying a view
5. The deposion of radiaon in land, air, water
6. Lakes, rivers, oceans, groundwater are contaminated by substances,
making the water unusable for drinking, cooking,...
7. The water temperature in streams, rivers, lakes, or oceans change.
8. Earth’s surface is destroyed by pescides
Exercise 5. Give the correct form of the words in brackets.
1. We need to ________________ (protecon) our oceans by reducing plasc waste and overshing.
2. Pescides and chemical ferlizers can be ________________ (toxicity) to both the environment
and human health.
3. Her younger sister can be ________________ (annoy) when she behaves naughly.
4. You must read the ________________ (instruct) carefully before you use the new oven.
5. We were taken aback at the ________________ (drama) changes in our village; each home owns a
computer now.
6. It is always ________________ (interest) to watch the cubs at play.
7. My mother advised me to be careful in my ________________ (choose) of friends.
8. The ________________ (hot) makes everybody very drowsy during the lesson in class.
9. The couple came here at the special ________________ (invite) of the prime minister.
10. Please ________________ (low) the volume of your voice. I can even hear you from next door.
11. These men are armed and ________________ (dangerous), and should not be approached.
12. The latest ________________ (edit) of this book contains many illustrave pictures.
13. The giant panda is an ________________ (danger) species due to habitat loss and poaching.
14. The dodo bird went into ________________ (exnct) in the 17
th
century due to hunng and
habitat destrucon.

15. The rainforest is the ________________ (habitaon) of many species of animals and plants.
Exercise 6. Fill in the blanks with the correct preposions.
It is now almost certain that global warming has been directly caused (1) ________________ man’s
use of fossil fuels. This has led (2) ________________ an internaonal debate about what we should
do to reduce the negave eects (3) ________________ our acons and how we can make the planet
safe for our children’s children to live in. One consequence (4) ________________ this debate has
been to improve the level of “green” educaon in schools and this should result (5)
________________ greater awareness of this dicult issue in the long term. However, in the short
term there sll remains much to be done. The reason (6) ____________ this is that we need to
address causes (7) _____________ the immediate problem.
Exercise 7. Complete the sentence with the words in the box.
contaminated
untreated
dead
pollutant
radioacve
eects
dumped
aquac
sewage
poison
1. ________________ or wastewater should be treated before it is discharged into the river or ocean.
2. More and more waste and ________________ are poured into the water, the soil and the air.
3. The ________________ material is stored in a special radiaon-proof container.
4. Oil spills can cause the death of ________________ animals such as sh.
5. ________________ sewage can spread disease and contaminate drinking water sources.
6. Cholera is transmied through ________________ water.
7. The health ________________ of air polluon include heart disease, lung cancer, and asthma.8.
Carbon dioxide is a dangerous air.
9. Over 150,000 tonnes of waste are ________________ annually along the coastline.
10. Up to 100.000 sh were found ________________ along the river last week.
Exercise 8. Choose the best opon to complete the sentence.
1. She ________________ lunch by the me we arrived.
A. nished B. has nished C. had nished D. nishing
2. Bob will come soon. When Bob ________________, we will see him.
A. come B. will come C. will be coming D. comes
3. I will get home at 5:30. Aer I get home, I ________________dinner.
A. will have B. will be having C. had D. have
4. As soon as the taxi ________________, we will be able to leave for the airport.

A. arrives B. arrive C. will arrive D. arrived
5. I will go to bed aer I ________________ my work.
A. nish B. nished C. will nish D. Finishes
6. I ________________ here when you arrive tomorrow.
A. am B. had been C. could be D. will be
7. I am going to wait right here unl Jessica ________________.
A. comes B. will have come C. is coming D. came
8. As soon as the war ________________ over, there will be great joy throughout the land.
A. are B. will be C. is D. would be
9. Right now the de is low, but when the de comes in, the ship ________________ the harbor.
A. le B. will leave C. will have le D. leave
10. I am going to start making dinner before my wife ________________ home from work today.
A. get B. gets C. will get D. got
Exercise 9: Idenfy the underlined part that needs correcon.
1. When it raining. I usually go to school by bus.
A. When B. raining C. usually go D. by bus
2. I learned a lot of Japanese while I am in Tokyo.
A. I B. a lot of C. Japanese D. am
3. I have not been well since I return home.
A. have not been B. well C. return D. home
4. I’ll stay here unl will you get back.
A. I’ll B. here C. unl D. will you
5. When Sam was in New York, he stays with his cousins.
A. in New York B. he C. stays D. his cousins
6. Last night. I had gone to bed aer I had nished my homework.
A. Last night B. had gone C. aer D. my homework
7. I will call you before I will come over.
A, will call B. you C. before D. will come
8. Ever since I was a child, I had been afraid of dogs.
A. Ever since B. was C. had been D. afraid of
9. By the me I le my apartment this morning, someone looked for me.

A. le B. this morning C. someone D. looked for
10. Whenever Mark will be angry, his nose gets red.
A. Whenever B. will be C. gets D. red
Exercise 10: Mark the leer A, B, C or D to complete the following sentences.
1. I will call you before I ________________ over.
A. come B. will come C. will be coming D. came
2. Aer she graduates, she ________________ a job.
A. got B. will get C. had got D. get
3. When I ________________ him tomorrow, I will ask him.
A. saw B. have seen C. will see D. see
4. As soon as it ________________ raining, we will leave.
A. stops B. stop C. had stopped D. stopped
5. By the me he comes, we will have ________________ already.
A. leave B. leaving C. le D. leaves
6. Whenever I ________________ her, I say hello.
A. see B. will see C. will have seen D. saw
7. The next me I go to New York, I am going ________________ a ballet.
A. seeing B. see C. saw D. to see
8. I will never speak to him again so long as I ________________.
A. lives B. will live C. am living D. live
9. By the me Bill ________________to bed tomorrow, he will have had a full day and will be ready
for sleep.
A. had gone B. will go C. goes D. went
10. As soon as I nish my report, I will call you and we ________________ out for dinner.
A. went B. will go C. will have gone D. go
11. By the me I return to my country, I ________________ away from home for more than three
years.
A. would be B. will have been C. will be D. am
12. Aer he ________________ breakfast tomorrow, he will get ready to go to work.
A. will have had B. has C. will be having D. have
13. As soon as he nishes dinner, he ________________ the children for a walk to a nearby
playground.
A. will take B. takes C. will be taking D. took
14. When Bill gets home, his children ________________ in the yard.
A. played B. will play C. will be playing D. play
15. He will work at his desk unl he ________________ to another meeng in the middle of the
aernoon.
A. went B. go C. will go D. goes
Exercise 11. Choose the correct word A, B, C or D for each gap to complete the following passage.
Rivers are (1) ________________ of the world’s most important natural resources. Many cies are on
large rivers, and (2) ________________ every country has at least one river that (3)
________________ an important part in the lives of its people.
Besides transportaon, rivers (4) ________________ food, water for crops, water to drink, and
opportunies for recreaon for people who live along their (5) ________________. And in order to
get water for crops, engineers somemes build a dam across a river and let the water become a lake
(6) ________________ the dam. Then people can use their water not only to (7) ________________
elds but also to make electricity for homes and industries.
(8) ________________, the water oen becomes polluted when cies on river banks grow (9)
________________ size and the number of industries increases. We are learning that it is necessary
to (10) ________________ rivers clean if we want to enjoy the benets of natural resources.
1. A. one
B. ones
C. among
D. those
2. A. most
B. mostly
C. almost
D. about
3. A. takes
B. makes
C. occupies
D. plays
4. A. supply
B. provide
C. distribute
D. bring
5. A. banks
B. shores
C. sides
D. beaches
6. A. behind
B. on
C. below
D. under
7. A. take
B. irrigate
C. drain
D. give
8. A. Moreover
B. Therefore
C. Thus
D. However
9. A. of
B. about
C. in
D. for
10. A. keep
B. get
C. hold
D. maintain
Exercise 12. Read the passage about Air Polluon and nd the answers to the quesons below.
AIR POLLUTION
We are nowadays becoming more aware of polluon maers that aect dramacally our lives,
especially there is growing concern about air polluon. There are some reasons that lead to this kind
of polluon. Firstly, the development of industrial zones, factories and building construcon areas is
producing a large amount of dust and poisonous air. Especially in developing countries, people don’t
pay much aenon to the air treatment process which makes the air polluon even worse. Secondly,
because of the increasing urbanizaon, it can be easily seen that there is always a lot of trac in rush
hour and dust on the road these days. The smoke from vehicles and manufacturing exhaust increases
the amount of carbon dioxide in the air which makes US feel really hard to breathe. The
consequences are very bad. Smog and dust can do serious harm to our health, especially our lungs.
We have thousands of asthma and adult respiratory distress cases each year which raise concern
about the air quality. Moreover, acid rain is becoming more and more popular which damages crops
and elds. Many people believe that air polluon is also causing global warming and it is dicult to
improve the air without the eorts of all countries around the world.
1. According to the passage, where do a large amount of dust and poisonous air come from?
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. Do developing countries take the air treatment process into careful consideraon?
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. Why is it dicult for us to breathe when travelling on the roads or streets?
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. Which parcular part of our body is seriously aected by smog and dust?
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. What is the harmful eect of acid rain?
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. According to the passage, if all countries in the world ignore the air polluon condion, will it be
easy to make the air fresher?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 13. Read the passage, and choose the correct answer A, B, C or D for each queson.
Saving the Environment: One Home at a Time

Polluon can be seen not only throughout the world, but also in our own homes. It comes from
household chemicals, the amount of water people use and the waste people produce and throw
away. What can be done to stop this polluon? Surprisingly, a person can help save the environment
by doing simple things.
First, we need to recycle, which allows products to be used over and over again. Recycling can also
reduce the number of trees cut down to produce paper products. It takes very lile eort. It is not
hard to place plasc and glass boles, aluminum cans and paper in a bin. Anyone can do it.
Second, we need to watch the amount of water used in the home. It can be conserved by taking short
shower instead of baths, repairing leaky faucets, using the dishwasher or washing machine only when
fully loaded, or simply turning the faucet o while brushing your teeth.
Third, we need to reduce waste. We need to recycle whenever possible, but should also try to use this
waste eecvely. For example, grass clippings and food scraps can be made into compost for plants.
The average person produces 4.3 pounds of waste every day, but we can reduce that amount by
recycling and reusing.
If we do our part in our own homes, we can help keep the planet from becoming more polluted.
1. Polluon can be caused from the following sources except _____________.
A. house chemicals B. water from household
C. wastes D. water in rivers
2. Recycling can help us _____________.
A. never cut down trees B. use products again and again
C. place garbage bins easily D. produce more paper product
3. In order to save water, we can do all of the following things except _____________.
A. take short showers instead of baths
B. repair leaky faucets
C. fully use the washing machine
D. turn the faucet o while brushing your teeth
4. Recycling helps to reduce waste because _____________.
A. plants need to develop
B. a person can do it in his home
C. waste can be recycled and reused
D. an average man produces compost for plant
5. The word “It” in paragraph 2 refers to _____________.
A. recycling B. the number C. cung down D. eort
Exercise 14. Choose the correct opon to complete each sentence.
1. While _____________ work, I saw an old friend of mine.
A. I walking home from B. walking home from
C. walked home from D. walking homework
2. Before _____________, I brushed my teeth.
A. le my house B. I leaving my house
C. leaving my house D. my house leaving
3. I feel asleep _____________ TV.
A. while I watch B. while watching
C. while watched D. during I was watching
4. While _____________ about adverb clauses, a mild earthquake shook the classroom.
A. the teacher lecturing B. the teacher was lecturing
C. lecturing D. lectured
5. _____________, a dog chased us down the street
A. While running B. While we were running
C. We were running while D. While running we were
6. Since _____________ to New York, Linda has made many friends.
A. coming B. come C. she coming D. she comes to
7. Peter went back to school _____________ the phone.
A. aer john calling him on B. John had called him on
C. aer John had called him on D. aer John had called him
8. _____________ yesterday, we saw many deer.
A. While we hiking through the woods B. Hiking through the woods
C. During hiking through the woods D. Hiking through the woods we
9. _____________ the necessary qualicaons, she was not hired for a job.
A. Lacked B. When lacking C. Lacking D. Because lacking
10. Unable to run the enre 42 kilometers, she decided to drop out of the race, _____________ her a
heat stroke.
A. the fague from the intense heat almost gave
B. the fague from the intense heat having almost given
C. which the fague from the intense heat having almost given
D. the fague from the intense heat had almost given
11. _____________ the age of 21, he was able to gamble in Las Vegas.
A. When reached B. Reached C. As reaching D. Upon reaching
12. _____________, Martha was watching her favorite TV program.
A. While Penchant talking to his friend
B. While Penchant was talked to his friend
C. While Penchant was talking to his friend
D. Penchant was talking to his friend while
13. Before _____________ visit my brother and his family, I will need to nish all of my business
dealings with my clients.
A. leaving for North Dakota B. leaving for North Dakota to
C. le for North Dakota to D. I leaving for North Dakota to
14. _____________, the student won a $10 million loery.
A. While worked on the computer B. While working on the computer
C. While she working on the computer D. D. Working on the computer while she
15. _____________ Asian economic crisis, it has been very hard for Mai and her family to pay their
bills.
A. The B. Because the C. Since the D. Since
Exercise 15. Reorder the words to have correct sentences.
1. since/ years old. / she/ was/ She/ has learned/ English/ 12/
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. I/ working, / will/ When/I/ nish/ have dinner./
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. she/ the housework, / school/ will/ go/ to/ As soon as/ she/ nishes/
__________________________________________________________________________________
4. he/ Someone / a shower. / rang/ him/ when/ was taking/
__________________________________________________________________________________
5. she/ got/ pregnant, / working/ stopped/ Aer/ Mary/ hard. /
__________________________________________________________________________________
6. the beach/ will/ go/ to/ nish/ when/ their children/ The Browns/ studying. /
__________________________________________________________________________________
7. Just/ she/ came/ she/ went/ to/ the/ hospital. / as/ back/ to/ Australia, /
__________________________________________________________________________________
8. I / since/ have played/ old. / football/I/ was/ 7/ years/
__________________________________________________________________________________
9. when/ dinner/ she/ came. / We/ were having/
__________________________________________________________________________________
10. she/ as soon as/ the/ heard/ She/ cried/ news. /
__________________________________________________________________________________
11. clearly/ everything/ started/ before/ we/ She/ had explained/ our/ work. /
__________________________________________________________________________________
12. airport/ at/ the/ she/ by/ the/ me/I / will/ have waited/ arrives. /
__________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 16a. Read the situaon, consequence and give soluons to each situaon in our country.
No.
Situaon
Consequence
Soluon
1.
Vietnamese people tend to use
private transportaon.
Harmful gases released into
the environment.
______________________
______________________
______________________
______________________
2.
In the summer, the demand
for air condioners increases
sharply.
When used, air condioners
will radiate hot heat into the
environment and warm the
Earth, destroying the ozone
layer
______________________
______________________
______________________
______________________
______________________
3.
Many factories discharge
waste into the river to save on
waste treatment costs.
Aects people’s quality of life
and health.
______________________
______________________
______________________
______________________
4.
People throw garbage
Polluon of land, water, air.
______________________

indiscriminately.
______________________
______________________
______________________
Exercise 16b. Based on the suggesons in exercise 16 a, write a paragraph (about 150 words) giving
soluons to protect the environment in Viet Nam.
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
UNIT 8. SHOPPING
A. VOCABULARY
WORD
PRONNCIATION
MEANING
access (n)
/ˈækses/
nguồn để ếp cận, truy cập vào
E.g. You need a password to get access to the computer system. Bạn cần có mật khẩu để truy cập
vào hệ thống máy nh.
addicted (adj) (+ to)
/əˈdɪktɪd/
say mê, nghiện
E.g. She is addicted to music. Cô ấy nghiện âm nhạc.
adversement (n)
/ədˈvɜːtɪsmənt/
quảng cáo
E.g. She scanned the adversement pages of the newspapers. Cô ấy lướt qua các trang quảng cáo
trên báo.
bargain (v)
/ˈbɑːrɡən/
mặc cả
E.g. Anna oen bargains in the shops for hours. Anna thường mặc cả hàng giờ trong các cửa hàng.
complaint (n)
/kəmˈpleɪnt/
lời phàn nàn / khiếu nại
E.g. The most common complaint about this restaurant is about poor service. Khiếu nại thường gặp
nhất về nhà hàng này là về dịch vụ kém.
convenience (store)
/kənˈviːniəns stɔːr/
(cửa hàng) ện ích
E.g. There is a convenience store outside the library. Có một cửa hàng ện lợi bên ngoài thư viện.
customer (n)
/ˈkʌstəmər/
khách hàng
E.g. I’m a regular customer of this shop. Tôi là khách hàng thân thiết của cửa hàng này.
discount (n)(shop)
/ˈdɪskaʊnt ʃɒp /
(cửa hàng) hạ giá
E.g. They’re oering a 10% discount on all sofas this month. Họ đang giám giả 10% cho tất cả các
ghế xô pha trong tháng này.
display (n, v)
/dɪˈspleɪ/
sự trưng bày, bày biện, trưng bày
E.g. The exhibion gives local arsts an opportunity to display their work. Triển lãm mang đến cho
các nghệ sĩ địa phương cơ hội trưng bày tác phẩm của họ.
dollar store
/ˈdɒlər stɔːr/
cửa hàng đồng giá (một đô la)
E.g. Dollar store is a store where everything costs one dollar. Dollar store là cửa hàng mà mọi thứ
đều có giá một đô la.
fair (n)
/feər/
hội chợ
E.g. Let’s take the kids to the fair. Hãy đưa bọn trẻ đến hội chợ.
farmers’ market (n)
/ˈfɑːrmərz’ ˈmɑːrkɪt /
chợ nông sản
E.g. There’s a farmers’ market every Thursday from noon to 4 p.m. Có một phiên chợ nông sản vào
thứ Năm hằng tuần từ trưa đến 4 giờ chiều.
goods (n)
/ɡʊdz/
hàng hoá
E.g. The goods will be delivered within ten days. Hàng sẽ được giao trong vòng mười ngày.
home-grown (adj)
/ˌhəʊm ˈɡrəʊn/
tự trồng
E.g. We oen eat home-grown tomatoes. Chúng tôi thường ăn cà chua nhà trồng
home-made (adj)
/ˌhəʊm ˈmeɪd/
tự làm
E.g. Home-made jam is usually beer than the kinds you buy in the shops. Mứt nhà làm thường
ngon hơn mua ngoài ệm.
item (n)
/ˈaɪtəm/
món, hàng
E.g. There are plenty of vegetarian items on the menu. Có rất nhiều món chay trong thực đơn.
on sale
/ɒn seɪl/
đang (được bán) hạ giá
E.g. Shoes are on sale with £5 o. Giày đang được giảm giả £5.
open-air market
/ˌəʊpən ˈeər ˈmɑːrkɪt/
chợ họp ngoài trời
E.g. There’s a big open-air market here on Saturdays. Có một cái chợ họp ngoài trời lớn ở đây vào
thứ Bảy.
price tag (n)
/ˈpraɪs tæɡ/
nhãn ghi giá một mặt hàng
E.g. I got a shock when I looked at the price tag. Tôi đã bị sốc khi nhìn vào nhãn giá
schedule (n)
/ˈʃedjuːl/
lịch trình, thời gian biểu
E.g. I have a very exible work schedule. Tôi có một lịch trình làm việc rất linh hoạt
B. WORD FORMATION
Word
Related words
Transcripon
Meaning
access (n)
/ˈækses/
nguồn để ếp cận, truy cập vào
access (v)
/ˈækses/
đăng nhập, xâm nhập
accessibility (n)
/əkˌsesəˈbɪlə/
nh có thể ếp cận được
accessible
/əkˈsesəbl/
có thể ếp cận được
accession
/əkˈseʃn/
sự đến gần, sự ếp cận
addicted (adj) (to)
/əˈdɪktɪd/
say mê, nghiện
addict (v)
/ˈædɪkt/
nghiện, quá yêu thích
addicon (n)
/əˈdɪkʃn/
sự say mê, yêu thích
adversement (n)
/ədˈvɜːtɪsmənt/
sự quảng cáo, bài quảng cáo
adverse (v)
/ˈædvərtaɪz/
quảng cáo
adversing (n)
/ˈædvərtaɪzɪŋ/
hoạt động quảng cáo, nghề quảng
cáo
adverser (n)
/ˈædvərtaɪzər/
người hoặc công ty quảng cáo
complaint (n)
/kəmˈpleɪnt/
lời phàn nàn / khiếu nại
complain (v)
/kəmˈpleɪn/
phàn nàn
complainant (n)
/kəmˈpleɪntənt/
người thưa kiện, người phàn nàn
convenience
(store)
/kənˈviːniəns/
(cửa hàng) ện ích
convenient (adj)
/kənˈviːniənt/
ện ích, ện lợi
C. GRAMMAR
1. Adverbs of frequency (Trạng từ chỉ tần suất)
Trạng từ chỉ tần suất (Adverb of frequency) là trạng từ dùng để diễn tả mức độ thường xuyên hoặc tần
suất diễn ra của một hành động.
1.1. Các trạng từ chỉ tần suất thông dụng:
%
Adverb of frequency
Example
100 %
always
I always go to school on me.
90%
usually
We usually eat out on Sunday morning.
80%
normally/ generally
He normally gets good mark.
70%
oen/ frequently
I oen stay up late.
50%
somemes
My mother somemes goes out with her friends.
30%
occasionally
She occasionally goes to bed late.
10%
seldom
We seldom talk together.
5%
hardly ever/ rarely
My mother hardly ever gets angry.
0%
never
I never go to school late.
1.2. Vị trí trạng từ chỉ tần suất
Trạng từ chỉ tần suất thường xuất hiện ở 3 vị trí: trước động từ thường, sau trợ động từ, và sau
động từ TO BE.
- Đứng sau động từ TO BE
E.g. He is somemes late for school.
(Thỉnh thoảng anh ta đi học muộn.)
I don’t like her, she’s never on me.
(Tớ chả thích cô ta, cô ta chẳng bao giờ đúng giờ cả.)
Đứng trước động từ thường:
E.g. I oen go to the movie with my friends.
(Tớ thường đi xem phim với các bạn của tớ.)
I rarely see her even though we live in the same building.
(Tớ hiếm khi thấy cô ấy dù chúng tớ sống cùng 1 tòa nhà.)
Đứng giữa trợ động từ và động từ chính
E.g. I have never been abroad.
(Tôi chưa bao giờ ra nước ngoài.)
You should always check your message.
(Bạn nên thường xuyên kiêm tra n nhắn.)
* Chú ý: Các trạng từ chỉ tần suất (trừ always, hardly, ever và never) còn có thể xuất hiện ở đầu câu
và cuối câu. Vị trí đứng đầu câu được dùng với mục đích nhấn mạnh.
E.g. Our English teacher usually gives US many assignments.
→ Our English teacher gives us many assignments usually.
→ Usually, our English teacher gives us many assignments.
(Giáo viên Tiếng Anh của chúng tôi thường giao rất nhiều bài tập.)
2. Present simple for future events (Thì hiện tại đơn dùng cho các sự kiện ở tương lai)
2.1. Cấu trúc
a. Cấu trúc thì hiện tại đơn đối với động từ thường
Khẳng định
S + V-s/es
Phủ định
S + do/does + not + V
Nghi vấn
Do/Does + S + V?
b. Cấu trúc thì hiện tại đơn đối với động từ to be
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm

Khẳng định
S+ am/is/are + N/Adj
Phủ định
S + am/is/are + not + N/Adj
Nghi vấn
Am/Is/Are + S + N/Adj?
2.2. Cách dùng thì hiện tại đơn
a. Thì hiện tại đơn nói về một sự thật hiển nhiên, một chân lý đúng.
E.g. The Sun rises in the East and sets in the West.
(Mặt trời mọc ở hướng Đông và lặn ở hướng Tây.)
b. Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả một hành động lặp đi lặp lại như một thói quen ở hiện tại.
E.g. I get up early every morning.
(Tôi dậy sớm mỗi sáng.)
c. Thì hiện tại đơn diễn tả một việc sẽ xảy ra trong tương lai có lịch trình cụ thể (lịch chiếu phim, tàu
xe, thời gian biểu, sự kiện...)
E.g. The football match starts at 8 o’clock.
(Trận bóng sẽ diên ra lúc 8 giờ.)
Our ight takes o at 9 p.m, so we have to go early at least 1 hour.
(Chuyến bay của chúng ta sẽ cất cánh lúc 9 giờ tối vì vậy chúng ta phải đến sớm ít nhất 1
ếng.)
2.3. Dấu hiệu nhận biết thì hiện tại đơn
Thì hiện tại đơn trong câu thường có những từ sau:
Every day (mỗi ngày), every month (mỗi tháng), every week (mỗi tuần) ....
Always (luôn luôn)
Oen (thường xuyên)
Usually (thường)
Rarely (hiếm khi)
Generally (thông thường, như thường lệ)
Frequently (thườngxuyên) …
D. PRONUNCIATION
Clusters: /sp/ and /st/
1. /sp/
/sp/ = /s/ + /p/

/s/: mặt lưỡi chạm nhẹ vào lợi hàm răng trên, phần ngạc mềm được nâng lên.
Sau đó, hơi được đẩy thoát ra giữa mặt lưỡi và lợi hàm trên nhưng không tạo
ra độ rung ở cổ họng.
/p/: mím nhẹ hai môi và nâng ngạc mềm lên để chặn luồng khí trong miệng,
sau đó bật hơi để tạo ra mà không làm rung dây thanh trong cổ họng.
E.g.
speciality
spend
speak
sport
spare
spa
2. /st/
/st/ = /s/ + /t/
/s/: mặt lưỡi chạm nhẹ vào lợi hàm răng trên, phần ngạc mềm được nâng lên.
Sau đó, hơi được đẩy thoát ra giữa mặt lưỡi và lợi hàm trên nhưng không tạo
ra độ rung ở cổ họng.
/t/: đầu lưỡi chạm vào lợi hàm trên và nâng phần ngạc mềm lên để chặn luồng
khí trong miệng. Sau đó, bật mạnh hơi để tạo ra âm /t/ mà không làm rung dây
thanh.
E.g.
costume
star
stand
west
stylist
test
3. Sự khác nhau giữa /sp/ và /st/
Về mặt âm thanh: sự khác biệt của cụm phụ âm /sp/ và /st/ xuất phát từ sự khác biệt của vị trí môi và
lưỡi khi bật hơi phát âm âm /p/ và /t/.
- Với âm /p/ lưỡi thả lỏng nhưng hai môi lại mím nhẹ.
- Với âm /t/ đầu lưỡi lại chạm vào lợi hàm trên và hai môi hé mở.
/sp/
/st/
spill
sll
spy
style

Về mặt chính tả:
- Cụm phụ âm /sp/ được phát âm trong các từ có cụm chữ cái sp.
E.g. spill, spa, sport,...
- Cụm phụ âm /st/ được phát âm trong các từ có cụm chữ cái st.
E.g. sll, costume, longest,...
E. PRACTICE
Exercise 1. Look and put the word under the correct photo. Then pronounce it correctly.
stand
spaceship
statue
(train) staon
spider
star
Spain
spaghe
1. ________________
2. ________________
3. ________________
4. ________________
5. ________________
6. ________________
7. ________________
8. ________________
Exercise 2. Use single underline with the word containing /sp/ and double underline with the word
containing /st/. Then read the sentences aloud (pay aenon to the sound /sp/ and /st/).
1. They prepared a special dinner for their anniversary.
2. She climbed the stairs to her apartment on the third oor.
3. There are many dierent species of birds in the rainforest.
4. Be careful not to spill your drink on the table.
5. With a steady hand, he painted a detailed masterpiece.
6. The polician delivered a powerful speech to inspire the crowd.
7. The undercover agent worked as a spy to gather intelligence.
8. He felt a bit queasy in his stomach aer eang too much.
9. Her unique fashion style always caught people’s aenon.
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm
10. The astronaut oated in the vast expanse of outer space.
Exercise 3. Look at the photo and ll in the blank with a correct word starng with /sp/ or /st/.
Then read aloud the sentences. Pay aenon to the words containing /sp/ or /st/.
1.
The ____________ spun a delicate web to catch its prey.
2.
They enjoyed playing various ____________ like soccer and tennis.
3.
He srred the soup with a large ____________.
4.
She cooked a delicious plate of ____________ for dinner.
5.
The trac light turned red, and all the cars had to ____________.
6.
The night sky was lled with countless twinkling ____________.
7.
The diligent ____________ spent hours studying for the upcoming
exam.
8.
They skipped smooth ____________ across the surface of the lake.
9.
She told an engaging bedme ____________ to her young children.
10.
The actors prepared to go on ____________ for their opening night
performance.
Exercise 4. Complete the sentences with the words in the box.
access
farmers’
complaint
vegetarian
price
customer
discount
open-air market
opportunity
bargains
convenience
adversement
1. There’s a big ____________ here on Saturdays.
2. I got a shock when I looked at the ____________ tag.
3. You need a password to get ____________ to the computer system.
4. She scanned the ____________ pages of the newspapers.
5. Anna oen ____________ in the shops for hours.
6. The most common ____________ about this restaurant is about poor service.
7. There is a ____________ store outside the library.
8. I’m a regular ____________ of this shop.
9. There’s a ____________ market every Thursday from noon to 4 p.m.
10. There are plenty of ____________ items on the menu.
11. They’re oering a 10% ____________ on all sofas this month.
12. The exhibion gives local arsts an ____________ to display their work.
Exercise 5. Choose the correct answers.
1. Where can you buy meat?
a. baker’s b. local shop c. butcher’s
2. Where can you buy owers?

a. orist’s b. chemist’s c. photographer’s
3. Where can you buy magazines and newspapers?
a. ironmonger’s b. newsagent’s c. drugstore
4. Where can you buy food and vegetables?
a. greengrocer’s b. candy store c. bookshop
5. Where can you buy movie ckets?
a. bank b. library c. cinema
6. Where can you buy lipsck?
a. furniture store b. cosmecs store c. jewelry store
7. Where can you buy teddy bears?
a. fashion shop b. gi shop c. shoe store
8. Where can you buy stamps?
a. university b. college c. post oce
9. Where can you buy bread?
a. school b. zoo c. bakery
10. Where can you buy beefsteak?
a. park b. restaurant c. garden
11. Where can you buy peonies?
a. orist’s b. waiter’s c. singer’s
12. Where can you buy Detecve Conan manga volumes?
a. bookstore b. movie studio c. grocery
Exercise 6. Can you nd a ‘general’ word to describe each group of items below?
novel
food
drink
furniture
fruit
clothing
jewelry
ower
toy
pet
1. ____________ e.g. peaches, pineapples, blueberries.
2. ____________ e.g. dogs, cats, hamster mouses.
3. ____________ e.g. tables, chairs, desks.
4. ____________ e.g. dresses, shirts, shoes.
5. ____________ e.g. pizza, spaghe, soup.
6. ____________ e.g. tea, wine, milk.
7. ____________ e.g. rings, earrings, bracelets.
8. ____________ e.g. teddy bears, dolls, lego.
9. ____________ e.g. roses, lavenders, tulips.
10. ____________ e.g. The Count of Monte Cristo, Harry Poer, Sherlock Holmes.
Exercise 7. Choose the correct answers.
1. Andrea lives next door so we ____________ see her.
a. never b. oen c. rare
2. Nancy and I (30%) ____________ go out for coee together.
a. never b. frequently c. occasionally
3. We meet ____________ at the Annual General Meeng.
a. never b. every day c. yearly
4. My doctor ____________.
a. yearly checks my health
b. checks yearly my health
c. checks my health yearly
5. It (0%) ____________ rains here in the summer.
a. never b. somemes c. rare
6. ____________ we take the dog o his leash at the beach.
a. Somemes b. Never c. Rarely
7. My sister ____________ two days of school in a row.
a. oen has missed
b. has missed oen
c. has oen missed
8. My boyfriend and I take vacaons together quite ____________.
a. never b. hardly c. frequently
9. Andy (10%) ____________ gets to visit his cousins.
a. very oen b. very rare c. rarely
10. I don’t earn much because I ____________.
a. never went to college
b. went never to college
c. went to college never
Exercise 8. Complete the following sentences with the present simple tense to talk about future
events.
1. I ____________ (start) my new job next Monday.
2. They ____________ (travel) to Paris next month.
3. She ____________ (visit) her grandparents every summer.
4. The train ____________ (arrive) at 3:00 p.m.
5. We ____________ (have) a family reunion next weekend.
6. He ____________ (study) for his exam tomorrow.
7. The Sun ____________ (rise) in the East every morning.
8. They ____________ (go) to the beach on Saturday.
9. I ____________ (meet) Jane for lunch on Thursday.
10. The conference ____________ (begin) at 9:00 a.m.
Exercise 9. Write sentences about your own future plans using the present simple.
1. ____________ (I/ go) to the gym tomorrow.
2. ____________ (Mary/ have) a family dinner on Friday.
3. ____________ (She/ y) to London next week.
4. ____________ (He/ aend) a conference in November.
5. ____________ (Bill/ study) for their exams over the weekend.
Exercise 10. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the present simple for future events.
1. She ____________ (leave) for her vacaon on Friday.
2. The bus ____________ (arrive) at 3:15 p.m.
3. We ____________ (celebrate) Thanksgiving next month.
4. They ____________ (visit) their grandparents this weekend.
5. The store ____________ (close) at 9 p.m. tonight.
6. She ____________ (travel) to Paris next week.
7. They ____________ (arrive) at the party around 7 p.m.
8. I usually ____________ (visit) my grandparents on Sundays.
9. The concert ____________ (start) at 8 p.m. tomorrow.
10. The bus ____________ (leave) at 6 a.m. on Monday.
Exercise 11. Complete the text by lling in the correct word form.
My cousin, Peter, (1. have) ____________ a dog. It (2. be) ____________ an intelligent pet with a
short tail and big black eyes. Its name (3. be) ____________ Kiki and it (4. like) ____________ eang
pork. However, it (5. never/ bite) ____________ anyone; somemes it (6. bark) ____________ when
strange guests visit. To be honest, it (7. be) ____________ very friendly. It (8. not/like) ____________
eang fruits, but it (9. oen/ play) ____________ with them. When the weather (10. become)
____________ bad, it (11. just/ sleep) ____________ in his cage all day. Peter (12. play)
____________ with Kiki every day aer school. There (13. be) ____________ many people on the
road, so Peter (14. not/ let) ____________ the dog run into the road. He (15. oen/ take)
____________ Kiki to a large eld to enjoy the peace there. Kiki (16. somemes/ be) ____________
naughty, but Peter loves it very much.
Exercise 12. Read the text and ck True (T) or False (F).
A new shopping mall is opening in Nam’s neighborhood today. It is very dierent from the present
shopping area. All the shops are under one roof. There will be air-condioners, movie theaters,
restaurants and children's play areas. That will be very convenient, especially during the hot and
humid summer months. Customers will shop in comfort and won’t noce the weather.
Some people in the neighborhood, however, are not happy about the changes. The owners of the
small stores on Tran Phu Street think the mall will take their business. Some of the goods in the new
stores will be the same as the ones in the small shops, but the stores in the mall will oer a wider
selecon of products, some at cheaper prices. The residents and store owners have been concerned
about the new mall for a few months. They have organized a community meeng in order to discuss
the situaon.
Statements
True/
False
1. The mall was opened yesterday.
_________
2. The mall will be inconvenient during the hot and humid summer months.
_________
3. Everyone in the neighborhood is pleased about the new mall.
_________
4. It will be more comfortable to shop in the mall than in the present shopping area.
_________
5. Some of the stores on Tran Phu Street may have to close.
_________
Exercise 13. Read the text again and answer the quesons.
1. What is special about the new shopping mall?
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. What facilies are available in the shopping mall?
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. What do the small store owners think about the new shopping mall?
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. What kinds of goods will the stores in the mall oer?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 14. Read the text and decide which answer A, B, C, or D best lls each gap.
A corner shop or a convenience shop is a Brish tradion. It is a small (1) ___________ shop. We can
nd a comer shop at the end of a local street in many neighbourhoods in towns and cies across the
UK. The comer shop sells all kinds of household goods and simple food and drinks like snacks,
groceries, coee, so drinks. It (2) ___________ sells newspapers, magazines, and cigarees.
Convenience stores are originally from America. They are like the Brish comer shops. The only (3)
___________ is that convenience stores are oen open 24 hours. Probably the most well-known
convenience store is 7-Eleven. You can nd a convenience store at any residenal (4) ___________, a
lling staon, a railway staon, or alongside a busy road.
Today, there are convenience stores all over the world. Each country has its own (5) ___________ of
convenience stores as well as the global brand 7-Eleven. Both comer shops and convenience stores (6)
___________ things at higher prices than the supermarket, but they are much more convenient.
1. A. retail
B. mass
C. wholesale
D. convenient
2. A. generally
B. nally
C. also
D. too
3. A. good
B. dierence
C. benet
D. thing
4. A. land
B. houses
C. community
D. area
5. A. brand
B. design
C. demand
D. descripon
6. A. are
B. ask
C. sell
D. oer
Exercise 15 a. Make complete sentences with suggested words.
1. Susie/ be/ always/ kind/ others.
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. They/ not/ oen/ sell/ bread.
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. Usually/ she/ leave/ early/ but/ she/ stay/ at work/ today.
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. This/ type/ exercise/ always/ give/ me/ headache.
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. Marina/ seldom/ go/ out.
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. Vegetarians/ never/ eat/ meat.
___________________________________________________________________________________
7. He/ be/ rarely/ see/ home/ holidays.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 15 b. Write in complete sentences using present simple tense.
1. she/ not/ sleep late/ weekend days
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. we/ not/ believe/ ghosts
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. you/ understand/ queson?
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. they/ not/ work late/ Fridays.
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. David/ want/ coee?
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. she/ have three/ daughter.
___________________________________________________________________________________
7. when/ she/ go to/ English class?
___________________________________________________________________________________
8. why/ he/ have to/ clean up?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 16. Write about your shopping habits based on the prompts from the quesons below.
Do you like (going) shopping? (Why? /Why not?)
How much me do you usually spend shopping?
How oen do you go shopping?
Where do you usually go shopping? With whom?
Which products do you spend the most money on? Why?
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
UNIT 9. DISASTERS
A. VOCABULARY
WORD
PRONNCIATION
MEANING
authority (n)
/ɔːˈθɒrə/
chính quyền, quyền lực
E.g. A policeman has the authority to arrest lawbreakers. Một cảnh sát có quyền bắt giữ những
người vi phạm pháp luật.
damage (n, v)
/ˈdæmɪdʒ/
thiệt hại, gây tổn hại
E.g. The accident caused no damage. Vụ tai nạn không gây thiệt hại.
destroy (v)
/dɪˈstrɔɪ/
phá huỷ
E.g. The earthquake damaged countless homes. Trận động đất đã phá hủy vô số ngôi nhà.
disaster (n)
/dɪˈzæstər/
thảm hoạ, thiên tai
E.g. They provided more than $2.3 billion in disaster relief. Họ đã cung cấp hơn 2,3 tỷ đô la cứu trợ
thiên tai.
earthquake (n)
/ˈɜːθkweɪk/
trận động đất
E.g. The earthquake measured 68 on the Richter scale. Trận động đất mạnh 68 độ Richter.
emergency kit
/ɪˈmɜːdʒənsi kɪt/
bộ dụng cụ dùng trong trường hợp khẩn cấp
E.g. Her family never went anywhere without an emergency kit. Gia đình cô không bao giờ đi đâu
mà không có bộ dụng cụ khẩn cấp.
erupt (v)
/ɪˈrʌpt/
phun trào
E.g. The volcano could erupt at any me. Núi lửa có thể phun trào bất cứ lúc nào.
Fahrenheit (n)
/ˈfærənhaɪt/
độ F (đo nhiệt độ)
E.g. Temperatures tomorrow will rise to around 70 degrees Fahrenheit. Nhiệt độ ngày mai sẽ tăng
lên khoảng 70 độ F.
funnel (n)
/ˈfʌnl/
cái phễu
E.g. I need a funnel to pour petrol into the tank. Tôi cần một cãi phễu để đổ xăng vào bình.
landslide (n)
/ˈlændslaɪd/
vụ sạt lở đât
E.g. The house was buried beneath a landslide. Ngôi nhà bị chôn vùi dưới một trận lở đất.
liquid (n)
/ˈlɪkwɪd/
chất lỏng
E.g. She poured the dark brown liquid down the sink. Cô ây đổ chât lỏng màu nâu sậm xuống bồn
rửa.
predict (v)
/prɪˈdɪkt/
dự đoán
E.g. They found out a reliable method of predicng earthquakes. Họ đã m ra một phương pháp
đáng n cậy để dự đoán động đất.
prey (adv)
/ˈprɪ/
khá là
E.g. It’s prey hard to explain. Điều đó khá khó để giải thích.
property (n)
/ˈprɒpə/
của cải, nhà cửa
E.g. Be careful not to damage other people’s property. Hãy cẩn thận để không làm hỏng tài sản của
người khác.
pull up
/pʊl ʌp/
kéo lên, nhổ lên, lôi lên
E.g. Please pull up a chair and join the conversaon. Hãy kẻo ghế lại đây và tham gia cuộc trò
chuyện.
rescue worker (n)
/ˈreskjuː wɜːrkər/
nhân viên cứu hộ
E.g. Rescue workers are helping people in ooded area. Lực lượng cứu hộ đang hỗ trợ người dân
vùng lũ.
Richter scale (n)
/ˈrɪktər skeɪl/
độ rích te (đo độ mạnh của động đất)
E.g. An earthquake measuring 7.1 on the Richter scale damaged countless houses in this city. Một
trận động đất mạnh 7,1 độ Richter đã làm hư hại vô số ngôi nhà trong thành phố này.
shake (v)
/ʃeɪk/
rung, lắc
The whole house shakes when a train goes past. Cả ngôi nhà rung chuyển khi một đoàn tàu chạy
qua.
storm (n)
/stɔːrm
bão
E.g. Her home was hit by two tropical storms. Nhà của cô ấy đã bị hai cơn bão nhiệt đới tấn công.
suddenly (adv)
/ˈsʌdənli/
đột nhiên, bỗng nhiên
E.g. It suddenly rained heavily. Trời đột ngột mưa to.
tornado (n)
/tɔːrˈneɪdəʊ/
lốc xoáy
E.g. The tornado pulled up the old tree by its roots. Cơn lốc xoáy kéo bật gốc cây cổ thụ.
tremble (v)
/ˈtrembl/
rung lắc
E.g. The babies began to tremble uncontrollably. Những đứa trẻ bắt đầu run rẩy không thể kiểm
soát.
tsunami (n)
/tsuːˈnɑːmi/
trận sóng thần
E.g. The tsunami caused immeasurable damage. Trận sóng thần gây ra thiệt hại khôn lường.
vicm (n)
/vɪktɪm/
nạn nhân
E.g. Rescue workers are trying to idenfy vicms of the landslide. Các nhân viên cứu hộ đang cố
gắng xác định danh nh các nạn nhân của vụ lở đất.
volcanic (adj)
/vɒlˈkænɪk/
thuộc / gây ra bởi núi lửa
E.g. The volcanic lava solidies as it cools. Dung nham núi lửa đông đặc lại khi nó nguội đi.
warn (v)
/wɔːrn
cảnh báo
E.g. The local people weren’t warned about the danger of this storm. Người dân địa phương không
được cảnh báo về sự nguy hiểm của cơn bão này.
B. WORD FORMATION
Word
Related words
Transcripon
Meaning
accommodaon (n)
/əˌkɒməˈdeɪʃn/
chỗ ở
accommodate (v)
/əˈkɒmədeɪt/
làm cho thích nghi
erupt (v)
/ɪˈrʌpt/
phun trào
erupon (n)
/ɪˈrʌpʃn/
sự phun (núi lửa)
erupve (adj)
/ɪˈrʌptɪv/
nổi lên, bùng lên
evacuate (v)
/ɪˈvækjueɪt/
di tản, di cư
evacuaon (n)
/ɪˌvækjuˈeɪʃn/
sự di tản, sự tản cư
evacuee (n)
/ɪˌvækjuˈiː/
người tản cư
storm (n)
/stɔːrm/
bão
storm (v)
/stɔːrm/
đột chiếm
stormy (adj)
/stɔːrmɪ/
có bão
volcano (n)
/vɒlˈkeɪnəʊ/
núi lửa
volcanic (adj)
/vɒlˈkænɪk/
thuộc núi lửa
suddenly (adv)
/ˈsʌdənli/
đột nhiên, bỗng nhiên
sudden (adj)
/ˈsʌdn/
đột ngột
C. GRAMMAR
PAST CONTINUOUS (THÌ QUÁ KHỨ TIẾP DIỄN)
1. Cách sử dụng
- Thì quá khứ ếp diễn dùng để diễn tả 1 hành động đang diễn ra tại một thời điểm xác định trong quá
khứ.
E.g. At seven o’clock yesterday, I was studying with my daddy.
(Vào lúc bảy giờ ngày hôm qua, tôi đang học với bố của tôi.)
- Dùng thì quá khứ ếp diễn để diễn tả 1 hành động đang diễn ra thì một hành động khác xen vào.
Hành động đang diễn ra chúng ta chia ở quá khứ ếp diễn, hành động xen vào ta chia ở quá khứ đơn.
Thường dùng với when/while.
E.g. I was talking to my mom when you called me last night.)
(Tôi đang nói chuyện với mẹ thì bạn gọi cho tôi tối hôm qua.)
- Thì quá khứ ếp diễn dùng để diễn tả 2 hành động xảy ra cùng lúc trong quá khứ.
E.g. I was reading my book while my friend was watching TV.
(Tôi đang đọc sách trong khi bạn tôi đang xem vi.)
2. Cấu trúc
Khẳng định
S + was/were + V-ing
Phủ định
S + was/ were + not + V-ing
Nghi vấn
Was/ Were + S + V-ing?
E.g. Mark was playing table tennis with his dad at 7 p.m. last night.
(Mark đang chơi bóng bàn với bố của anh ấy lúc 7 giờ tối hôm qua.)
Mark wasn’t playing table tennis with his dad at 7 p.m. last night.
(Mark không chơi bóng bàn với bố cùa anh ấy lúc 7 giờ tối hôm qua.)
Was Mark playing table tennis with his dad at 7 p.m. last night?
(Có phải Mark đang chơi bóng bàn với bố của anh ấy lúc 7 giờ tối hôm qua không?)
3. Dấu hiệu nhận biết
Có thể dễ dàng nhận biết được thì quả khứ ếp diễn khi trong câu có các trạng từ chỉ thời điểm xác
định trong quá khứ.
- At + giờ chính xác + thời gian ở quá khứ (At 8 a.m. yesterday)
- At + this me + thời gian ở quá khứ (At this me three months ago,...)
- In + năm xác định (in 2004, in 2002)
- In the past (trong quá khứ)
D. PRONUNCIATION
STRESS IN WORDS ENDING IN -AL AND -OUS (TRỌNG ÂM CỦA CÁC TÙ KÉT THÚC BANG ĐUÔI -AL VÀ -OUS)
1. Các nh từ/ danh từ kết thúc bằng đuôi -al
Một số nh từ và danh từ được hình thành bằng cách thêm đuôi -al vào sau danh từ hoặc động từ.
Thông thường việc thêm đuôi -al không làm thay đổi trọng âm của danh từ hoặc động từ gốc.
E.g.
Danh từ/ động từ gốc
Tính từ/ danh từ đuôi -al
naon /ˈneɪʃn/
→ naonal /ˈnæʃnəl/
propose /prəˈpəʊz/
→ proposal /prəˈpəʊzl
nature /ˈneɪtʃər/
→ natural /ˈnætʃrəl/
Tuy nhiên vẫn có một số trường hợp ngoại lệ
Danh từ/ động từ gốc
Tính từ/ danh từ đuôi -al
commerce /ˈkɒmɜːs/
→ commercial /kəˈmɜːʃl/
2. Tính từ kết thúc bằng đuôi -ous:
Một số danh từ khi thêm đuôi -ous sẽ biến thành nh từ.
- Thường thì trọng âm của từ đó nằm ở âm ết trước đuôi -ous.
E.g. Famous /ˈfeɪməs/: nổi ếng
Enormous /i’no:rmos/: to lớn, khổng lồ
- Tuy nhiên, có một số từ có trọng âm khác nhau.
E.g. Poisonous /ˈpɔɪzənəs/: có độc, độc hại
Dangerous /ˈdeɪndʒərəs/: nguy hiểm
Humorous /ˈhjuːmərəs/: hài hước, hóm hỉnh
Marvellous /ˈmɑːrvələs/: kỳ lạ, tuyệt diệu
E. PRACTICE
Exercise 1. Mark the stress of the words in the box then put them in the blanks and say the
sentences aloud.
laborious
emoonal
marvelous
natural
enormous
chemical
social
glamorous
1. The skyscraper’s ______________ height dominated the city skyline, making it impossible to miss
from any angle.
2. The waterfall was surrounded by lush greenery and wildlife, creang a peaceful and
______________ oasis in the heart of the forest.
3. The red carpet event was a ______________ aair, with celebries and dignitaries arriving in
elegant are and sparkling jewelry.
4. The local community center hosted a variety of ______________ events, bringing together people
from all walks of life for shared acvies and conversaons.
5. The scienst conducted a series of complex ______________ experiments in the laboratory, aiming
to discover new compounds with unique properes.
6. The hearelt speech delivered by the bride’s father brought tears to everyone’s eyes, evoking
strong ______________ reacons from the enre audience.
7. The sunset over the ocean was a ______________ display of vibrant colors, leaving everyone in
awe of nature’s beauty.
8. The construcon of the intricate model ship proved to be a ______________ task, requiring hours
of meculous work.
Exercise 2. Circle the word with a dierent stress paern from the others.
1. A. emoonal
B. nature
c. injure
D. climate
2. A. laborious
B. tropical
C. debris
D. document
3. A. chemical
B. destroy
C. erupt
D. exploit
4. A. documentary
B. preparaon
C. scienc
D. raonal
5. A. erupon
B. visual
C. destroy
D. volcano
6. A. remember
B. chemical
C. expression
D. convenient
7. A. personal
B. computer
C. formaon
D. connecon
8. A. naonal
B. cultural
C. popular
D. enormous
9. A. successful
B. humorous
C. arrangement
D. aracve
10. A. construcon
B. typical
C. glorious
D. purposeful
Exercise 3. Look at the pictures and put the words/ phrases in the spaces provided.
ood
forest re
volcanic erupon
drought
tsunami
hurricane
tornado
earthquake

1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Exercise 4. Match the words in column A to their denions in column B.
A
B
1. volcanic erupon
A. a mass of earth, rock, etc. that falls down the slope of a mountain or
a cli
2. earthquake
B. a long period without rain
3. thunderstorm
C. an extremely large wave in the sea caused, for example, by an
earthquake
4. landslide
D. a large amount of water spread from a river, sea etc. that covers an
area that is normally dry
5. sandstorm
E. a disaster that a volcano explodes and throws out re, lava, smoke
etc.
6. tornado
F. a re in the forest caused by high temperature
7. ood
G. a sudden violent movement of the ground
8. drought
H. a storm in a desert in which sand is blown into the air by strong
winds
9. tsunami
I. a storm with thunder and lightning and usually very heavy rain
10. wildre
J. a strong wind that blows in a circle
Answer:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Exercise 5. Choose the correct answer A, B, C or D to complete each sentence.
1. She is good ______________ meteorology.
A. on B. in C. at D. for
2. Last night, volcano Maui ______________ and the large areas of land were aected.
A. erupts B. erupted C. erupng D. erupt
3. When a volcanic erupon occurs, the hot ______________ pours downhill.
A. ash B. smoke C. dirt D. lava
4. Since there are two villages located at the foot of the volcano, the local populaon was
__________.
A. evacuated B. killed C. died D. injured
5. The earthquake ______________ have been sent humanitarian aid by many countries.
A. vicms B. elders C. rescuers D. soldiers
6. When there is a plane crash, a lot of ______________ is le.
A. dust B. debris C. waste D. piece
7. A powerful ______________ o the coast of Indonesia sparked a three-metre-high wave and killed
at least 113 people.
A. earthquake B. tornado C. tsunami D. landslide
8. A ______________ oen occurs in the mountainous areas because many trees have been cut
down.
A. forest re B. ood C. tornado D. landslide
9. ______________ oen happen in rainy season especially in the center of Vietnam.
A. Droughts B. Storms C. Floods D. Sandstorms
10. Deforestaon leads to ______________ which can be dened as the changes in the average
temperature.
A. ood B. climate change C. sandstorm D. erosion
Exercise 6. Fill in the blank with the correct form of the words in parentheses.
1. Today ______________ can predict when a dal wave will hit land. (SCIENCE)
2. That tsunami was the most ______________ of the year 2004. (DISASTER)
3. We had le the city ______________ before dal waves came. (SAFETY)
4. Thousands of people have been made ______________ by the ooding. (HOME)
5. Thunder makes me ______________. (TERRIFY)
6. The ______________ of the volcanoes is always disastrous. (ERUPT)
Exercise 7. Choose the best answer A, B, C or D to complete each sentence.
1. They ______________ on the lake when it started to rain so they went home.
A. shed B. shing C. were shing D. are shing
2. Her dad found some money while he ______________ her suitcase.
A. packing B. package C. are packing D. was packing
3. Your brother ______________ in Myanma when he met his girlfriend.
A. study B. was studying C. were study D. was study
4. His grandma tried cake for the rst me while she ______________ in China.
A. staying B. is staying C. is stayed D. was staying
5. Her mom ______________ in the park when she saw a tree.
A. was going B. was going C. were going D. were going
6. _______it _______ when I woke up this morning?
A. Is...raining B. Was.. .raining C. Is...rain D. Were.. .raining
7. What ______________ when his mother came?
A. were you doing B. was you doing C. are you doing D. are you doing
8. What did you watch on TV while you ______________ dinner last night?
A. were having B. was having C. were having D. was having
9. The policeman ______________ his leer in the post oce at that me.
A. is sending B. was sending C. sending D. was sending
10. It ______________ and cloudy when I le Ireland.
A. was rain B. was raining C. is raining D. raining
Exercise 8. Give the correct form of the verbs in the past connuous tense.
1. At this me last year, they ______________ (build) this stadium.
2. I ______________ (drive) my motorbike very fast when James called me.
3. I ______________ (chat) with Hannah while Mr. Henry ______________ (teach) the lesson
yesterday.
4. My brother ______________ (watch) TV when I got home.
5. At this me last night, I ______________ (prepare) for my husband’s birthday party.
6. What ______________ (you/ do) at 7 p.m. last Monday?
7. Where you ______________ (go) when I saw you last weekend?
8. They ______________ (not go) to church when I met them yesterday.
9. My mother ______________ (not do) the housework when our grandparents came home.
10. Ms. Stacey ______________ (read) books while her children ______________ (play) football
yesterday aernoon.
Exercise 9: Give the correct form of the verbs in brackets: past simple or past connuous.
1. When I _________ to school, I _________ John. (walk/see)
2. When I _________ in the kitchen, Mary _________. (help/come)
3. While she _________ the soup, the children _________. (cook/play)
4. While they _________ cards, the baby _________. (play/sleep)
5. When I _________ in the garden, my uncle _________. (work/call)
6. Carol _________ TV while Bob and Peter _________ football. (watch/play)
7. When she _________ her hair, the baby _________ to cry. (wash/begin)
8. A strong wind _________ when the plane _________. (blow/land)
9. When she _________ tennis, it _________ to rain. (play/began)
10. When I _________ TV, the lights _________ out. (watch/go)
11. While he _________ the piano, she _________ to him. (play/listen)
12. While she _________ up her room, he _________ his car. (dy/wash)
13. The boys _________ in the garden while she _________ the owers. (help/water)
14. He _________ Mary when he _________ through the park. (meet/walk)
15. We _________ computer games while she _________ a book. (play/read)
Exercise 10: Give the correct form of the verbs in brackets: past simple or past connuous.
1. They _________ (have) tea when the doorbell _________ (ring).
2. Father _________ (smoke) his pipe while mother _________ (read) a magazine.
3. While he _________ (mow) the lawn, it _________ (start) to rain.
4. He _________ (have) breakfast when the toaster _________ (blow) up.
5. When I _________ (come) into the oce, my boss _________ (wait) for me.
6. When we _________ (see) Brian, he _________ (drive) a taxi.
7. He _________ (wait) in the car while she _________ (do) the shopping.
8. When he _________ (arrive), we _________ (have) dinner.
9. While they _________ (play) chess, we _________ (go) shopping.
10. They _________ (have) a party while he _________ (sleep).
11. He _________ (take) a photo when I _________ (feed) the ducks.
12. They _________ (play) football when the lights in the stadium _________ (go) out.
13. While George and John _________ (clean) their room, Linda _________ (do) the ironing.
14. Sam _________ (do) the ironing when Jack _________ (phone) her.
15. We _________ (wait) at Victoria staon when the train _________ (arrive).
Exercise 11. Read the text and choose the correct opon.
Erosion in America
Erosion of America’s farmland by wind and water has been a problem since selers rst put the
prairies and grasslands under the plow in the nineteenth century. By the 1930s, (1) _____________
282 million acres of farmland (2) _____________ by erosion. Aer 40 years of (3) _____________
eorts, soil erosion has accelerated due to new demands (4) _____________ on the land by heavy
crop producon. In the years ahead, soil erosion and the polluon problems it causes are likely to
replace petroleum scarcity as the naon’s most crical (5) _____________ resource problem.
1. A. more than
B. more
C. less
D. than
2. A. damaged
B. was damaged
C. were damaged
D. damages
3. A. conserve
B. conservaon
C. conserving
D. conservaons
4. A. were placed
B. was placed
C. which placed
D. placed
5. A. nature
B. natural
C. naon
D. naonal
Exercise 12. Read the text and then choose the best answer A, B, C or D.
Two of the most dangerous storms which aect America are hurricanes and tornadoes. They are very
much feared by anyone who may live in the path of their destrucon.
Every year homes are destroyed by their fury and oen lives are lost. Most people who live near the
coast are forced to evacuate their homes and to move to safer areas unl the storm passes. Floods
are caused along the coasts by both the heavy rain and a storm de that is considerably above normal
water level. The high winds, coastal ooding and heavy rains associated with a hurricane cause
enormous damage.
Hurricanes usually develop between July and October. Once they hit the land, they carry tremendous
power with driving rain and wind.
Tornadoes are violent low-pressured storms. These storms occur most oen during the summer
months and are noceable by their strong wind and lack of rain. The sky turns black as dust is sucked
up into the air. Tornadoes are capable of liing quite heavy objects from the ground. They can pick up
trees and cars right
into the air and even upli heavier objects such as homes and railway cars.
Both hurricanes and tornadoes cause millions of dollars worth of damage to life and property every
year. Today they can be predicted more easily than in the past, but they cannot be stopped or
ignored.
1. What are two of the most dangerous storms which aect America?
A. Thunderstorms and hurricanes. B. Typhoons and thunderstorms.
C. Hurricanes and tornadoes. D. Hurricanes and typhoons.
2. At which part of the year do hurricanes usually develop?
A. July and August only. B. Between July and October.
C. From the seventh to the ninth month. D. All the year round.
3. What is the major similarity of both a hurricane and a tornado?
A. They cover only a small area. B. They have either wind or speed.
C. They are not accompanied by rain. D. They can cause great damage.
4. Which of the following is true of tornadoes and hurricanes?
A. They cannot be predicted with accuracy.
B. They are easier to control today than in the past.
C. Tornadoes are more dangerous than hurricanes.
D. They can be predicted today with greater accuracy.
5. Which of the following was not menoned in the arcle?
A. The damage caused by hurricanes and tornadoes.
B. The tremendous power of these storms.
C. The number of people killed each year by these storms.
D. The me of year when they are most likely to strike.
Exercise 13. Choose the correct word A, B, C or D for each gap to complete the following passage.
More than a billion people all over the world are (1) _____________ the threat of desert expansion,
but few of them are aware that they themselves cause it and are also its (2) _____________. People
cut (3) _____________ trees for fuel and farmland. Their herds eat (4) _____________ the grass
covering valley oors and hillsides. The climate and soil quality, therefore, are aected and forests are
turned into (5) _____________.
In some places, many people had to leave their homes when their wells became dry and sand buried
their house and crops. Therefore, governments in nearby areas have helped local people (6)
_____________ trees and banned burning rewood for fuel. Many other techniques have been (7)
_____________. For example, in Iran, a thin covering of oil was poured on sandy areas to retain (8)
_____________ for planng trees, but this method may harm the environment. Other countries built
long canals or pipelines (9) _____________ water to desert areas.
Unless people nd more (10) _____________ methods, their homes and land will be lost. The ght
against the desert is connuing.
1. A. under
B. in
C. on
D. of
2. A. enemies
B. vicms
C. friends
D. eects
3. A. o
B. back
C. in
D. down
4. A. away
B. up
C. into
D. out
5. A. blanks
B. spaces
C. deserts
D. bareness
6. A. planng
B. to plant
C. plant
D. planted
7. A. using
B. use
C. uses
D. used
8. A. water
B. soil
C. earth
D. ferlizer
9. A. take
B. to carry
C. fetch
D. bring
10. A. eecve
B. great
C. major
D. useful
Exercise 14. Write in full sentences using the past connuous tense.
1. They/ play/ tennis/10.30 yesterday morning.
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. Ann/ do/ homework/ 5 o’clock this aernoon.
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. My father/ wash/ car/ from ve to six.
__________________________________________________________________________________
4. This me last year/ we/ live/ France.
__________________________________________________________________________________
5. The students/ oer/ owers/ the visitors.
__________________________________________________________________________________
6. I/ cook/ dinner/ half an hour ago.
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm
__________________________________________________________________________________
7. She/ work/ the studio/ that me.
__________________________________________________________________________________
8. What/ you/ do/ from 3 to 6 yesterday aernoon?
__________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 15. Write in full sentences using the past connuous tense or the past simple tense.
1. I/ shop/ when/ Linda/ call/ me/.
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. My brother/ do/ homework/ 9 o’clock/.
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. He/ eat/ lunch/ when/ we/ arrive/.
__________________________________________________________________________________
4. she/ live/ Hue/ that me/?
__________________________________________________________________________________
5. She/ play/ guitar/ 6 p.m.
__________________________________________________________________________________
6. she/ type/ a leer/ when/ her boss/ go/ into/ meeng room/?
__________________________________________________________________________________
7. While/ she/ watch/ TV, / she/ hear/ the doorbell/.
__________________________________________________________________________________
8. she/ study/ English/ 8 p.m./ yesterday/?
__________________________________________________________________________________
9. She/ see/ accident/ while/ she/ watch/ television/.
__________________________________________________________________________________
10. What/ your lile/ brother/ do/ this me/ yesterday/?
__________________________________________________________________________________
11. The doorbell/ ring/ while/ she/ eat/ lunch/.
__________________________________________________________________________________
12. your friends/ drink/ juice/ when/ you/ arrive/?
__________________________________________________________________________________
13. What/Asley/ do/ while/ her sister/ go/ Ha Noi/?
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm
__________________________________________________________________________________
14. 9 o’clock/ last Sunday, /I/ do/ homework/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 16. Storms and oods are the most common natural disasters in Viet Nam and they caused
severe damage. Write a paragraph about the problem of storms and oods in our country, then
present the soluon.
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
UNIT 10.
COMMUNICATION IN THE FUTURE
A. VOCABULARY
WORD
PRONNCIATION
MEANING
account(n)
/əˈkaʊnt/
tài khoản (ngân hàng, mạng xã hội...)
E.g. I sent the money into my savings account. Tôi đã gửi ền vào tài khoản ết kiệm của mình.
advanced (adj)
/ədˈvɑːnst/
ên ến
E.g. Sciensts are working on highly advanced technology to replace fossil fuels. Các nhà khoa học
đang nghiên cứu công nghệ ên ến để thay thế nhiên liệu hóa thạch.
carrier pigeon (n)
/ˈkæriər pɪdʒɪn/
bồ câu đưa thư
E.g. Carrier pigeon has been trained to carry message from one place to another. Chim bồ câu đưa
thư đã được huấn luyện để mang thông điệp từ nơi này đến nơi khác.
charge (v)
/tʃɑːdʒ/
nạp, sạc (pin)
E.g. Don’t forget to charge your phone before going out. Đừng quên sạc điện thoại trước khi ra
ngoài.
emoji (n)
/ɪˈməʊdʒi/
biểu tượng cảm xúc
E.g. He responded with a red heart emoji. Anh ấy đáp lại bằng biểu tượng cảm xúc trái m màu đỏ.
holography (n)
/ˈhɒləɡrɑːfɪ/
hình thức giao ếp bằng ảnh không gian ba
chiều
E.g. The holography exhibit at the science museum was incredibly impressive. Triển lãm ảnh không
gian ba chiều tại bảo tàng khoa học vô cùng ấn tượng.
instantly (adv)
/ˈɪnstəntli/
ngay lập tức
E.g. We can connect instantly via skype. Chúng ta có thể kết nối ngay lập tức qua skype.
Internet connecon
/ˈɪntənet kəˈnekʃn /
kết nối mạng
E.g. Free internet connecon is available in the room. Kết nối internet miễn phí có sẵn trong phòng.
language barrier
/ ˈlæŋɡwɪdʒ bæriər/
rào cản ngôn ngữ
E.g. The language barrier can be a big factor aecng understanding. Rào cản ngôn ngữ có thể là
một yếu tố lớn ảnh hưởng đến sự thông hiểu.
live (adj)
/laɪv/
(phát sóng, truyền hình) trực ếp
E.g. This club has live music most nights. Câu lạc bộ này có nhạc biểu diễn trực ếp hầu hết các tối.
smartphone (n)
/ˈsmɑːrəʊn/
điện thoại thông minh
E.g. You can use your smartphone to access the internet. Bạn có thể sử dụng điện thoại thông minh
của mình để truy cập internet.
social network (n)
/ˌsəʊʃl ˈnetwɜːrk/
mạng xã hội
E.g. We should teach children how to use social network eecvely. Chúng ta nên dạy trẻ cách sử
dụng mạng xã hội một cách hiệu quả.
tablet (n)
/ˈtæblət/
máy nh bảng
E.g. She bought her son a new tablet. Cô ấy mua cho con trai một chiếc máy nh bảng mới.
telepathy (n)
/təˈlepəθi
hình thức giao ếp bằng ý nghĩ, thần giao cách
cảm
E.g. He can communicate with her by telepathy. Anh ấy có thể giao ếp với cô ấy bằng thần giao
cách cảm.
text (v, n)
/tekst/
nhắn n, văn bản
E.g. She is texng. Cô ấy đang nhắn n
thought (n)
/θɔːt/
ý nghĩ
E.g. I can read her thought. Tôi có thể đọc được suy nghĩ của cô ta.
translaon machine
/trænzˈleɪʃn məˈʃiːn /
máy dịch thuật
E.g. We can use translaon machine to translate this document. Chúng tôi có thể sử dụng máy dịch
để dịch tài liệu này.
transmit (v)
/trænzˈmɪt/
truyền, chuyển giao
E.g. Signals of the match transmied from a satellite. Tín hiệu của trận đấu được truyền từ vệ nh.
video conference
/ˈvɪdiəʊ kɒnfərəns/
cuộc họp trực tuyến
E.g. He reported his work to the execuve board of the company by video conference. Anh ấy đã
báo cáo công việc của mình với ban điều hành của công ty qua cuộc họp trực tuyến.
voice message
/ˈvɔɪs mesɪdʒ/
n nhắn thoại
E.g. You can leave him a voice message. Bạn có thể để lại cho anh ấy một n nhắn thoại.
webcam (n)
/ˈwebkæm
thiết bị ghi / truyền hình ảnh
E.g. He directs his business mostly from home via e-mail and webcam. Anh ấy chỉ đạo công việc
kinh doanh của mình chủ yếu từ nhà thông qua e-mail và webcam.
zoom (in / out) (v)
/zuːm
phóng (to), thu (nhỏ)
E.g. The camera zoomed in on the actor’s face. Máy ảnh phóng to khuôn mặt của nam diễn viên.
B. WORD FORMATION
Word
Related words
Transcripon
Meaning
communicate (n)
/kəˈmjuːnɪkeɪt/
giao ếp
communicaon (n)
/kəˌmjuːnɪˈkeɪʃn/
sự giao ếp
communicave
(adj)
/kəˈmjuːnɪkətɪv/
có nh chất giao ếp
interact (v)
/ˌɪntərˈækt/
tương tác
interacon (n)
/ˌɪntərˈækʃn
sự tương tác
interacve (adj)
/ˌɪntərˈæktɪv/
có nh tương tác
instantly (adv)
/ˈɪnstəntli/
ngay lập tức
instant (adj)
/ˈɪnstənt/
liền, ngay
telepathy (n)
/təˈlepəθi/
thần giao cách cảm
telepathic (adj)
/ˌtelɪˈpæθɪk/
thuộc về ngoại cảm
telepathically (adv)
/ˌtelɪˈpæθɪkli/
sử dụng thần giao cách cảm
thought (n)
/θɔːt/
ý nghĩ
think (v)
/θɪŋk/
suy nghĩ
transmit (v)
/trænzˈmɪt
truyền, chuyển giao
transmission (n)
/trænzˈmɪʃn/
sự chuyên giao,sự truyền phát
thanh
transmier (n)
/trænzˈmɪtər/
người hoặc máy truyền phát thông
n
C. GRAMMAR
1. Preposion of place and me
Giới từ chỉ thời gian và nơi chốn là hai chủ điểm ngữ pháp rất quan trọng trong ếng Anh. Trong đó,
giới từ chỉ nơi chốn (Preposion of Place) dùng để cung cấp thông n về địa điểm, vị trí của sự vật, sự
việc được nhắc tới. Giới từ chỉ thời gian
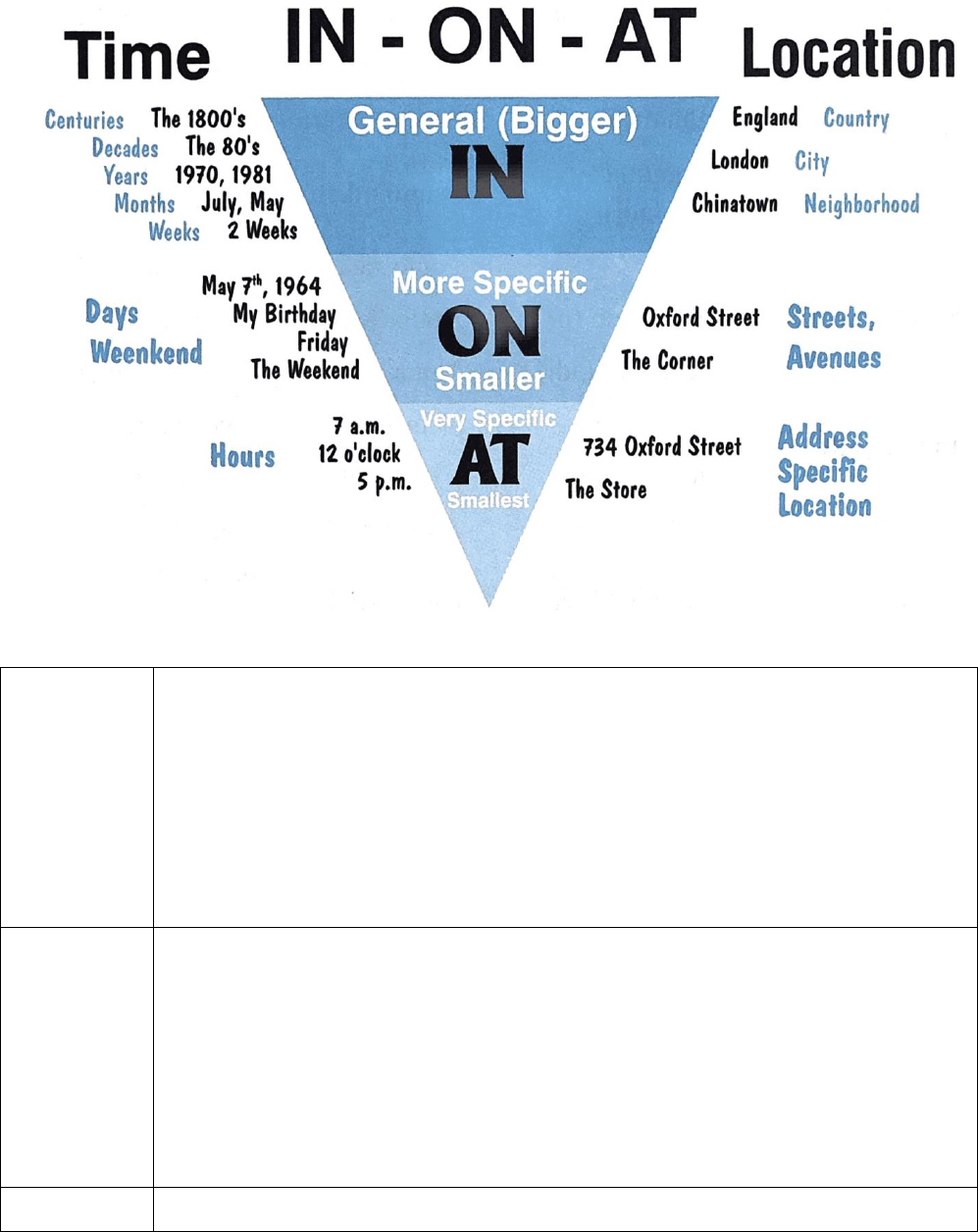
(Preposion of me) dùng để cung cấp các thông n về thời gian, giờ giấc hoặc thời điểm cụ thể.
Chúng ta sẽ cùng m hiểu cách sử dụng của tùng giới từ nhé.
a. Preposion of Time (giới từ chỉ thời gian)
In
- “In” đứng trước buổi trong ngày
E.g. in the morning, in the aernoon, in the evening
- “In” đứng trước năm, tháng, mùa, thế kỉ
E.g. in 1990, in May, in June, in summer, in fall, in spring, in 20
th
century...
- “In” đứng trước một khoảng thời gian là bao lâu
E.g. In 15 minutes, in one hour...
On
- “On” đứng trước ngày trong tuần.
E.g. on Monday, on Tuesday...
- “On” đứng trước ngày tháng trong năm.
E.g. on June 25
th
, on May 14
th
...
- “On” đứng trước ngày trong kì nghỉ hay các buổi trong ngày cụ thể.
E.g. on Christmas day, on Monday morning, on the weekend...
At
- “At” đứng trước giờ
E.g. at 9 o’clock, at 7 p.m...
- “At” đứng trước các thời điểm cụ thể
E.g. at night, at noon, at midnight, at the sunset, at the sunrise, at lunchme, at the
weekend, at Christmas
Aer
- Có nghĩa là “sau khi”
E.g. aer I got married, Aer 2 hours
Before
- Có nghĩa là “trước khi”
E.g. before 2010 before lunchme
From ... to
- Từ thời điểm này đến thời điểm kia
E.g. From Monday to Thursday From 8 a.m. to 10 p.m. tomorrow
Unl/ ll
- Cho đến khi
E.g. unl Friday, unl spring
During
- Trong suốt
E.g. during the war, during 2 weeks
b. Preposion of Place (giới từ chỉ nơi chốn)
In
(ở trong)
- “In” chỉ vị trí bên trong thành phố, đất nước hay một địa điểm phạm vi rộng.
E.g. in Ha Noi, in Viet Nam, in Asia...
- “In” đứng trước khoảng không gian khép kín như trong phòng, toà nhà, cái
hộp...
E.g. in the box, in the room, in the park...
- In đứng trước từ chỉ phương hướng
E.g. in the North, in the West, in the South...
On
(ở trên)
- “On” chỉ vị trí ở phía trên một bề mặt nào đó.
E.g. There are three apples on the table. (Có 3 quả táo ở trên bàn.)
- “On” dùng chỉ địa điếm nằm trên một con đường.
E.g. An’s house is on Chùa Láng Street. (Nhà của An ở trên phố Chùa Láng)
- “On” dùng vói phưong ện giao thông (trừ car, taxi)
E.g. She got on the last train. (Cô ấy lên chuyến tàu cuối cùng.)
It’s very noisy on the bus. (Ở trên xe bus rất ồn ào.)
- Tuy nhiên khi lên taxi hay ô tô, ta dùng “in”
E.g. She got in a car. (Cô ấy lên xe ô tô.)
We got in a taxi. (Chúng tôi lên xe taxi.)
At
(tại)
- “At” chỉ vị trí, địa điểm cụ thể.
E.g. I bought this book at Minh Thang bookstore. (Tôi mua cuốn sách này ở nhà
sách Minh Thắng.)
- “At” đứng trước địa điểm cụ thể có số nhà, tên đường.
E.g. She lives at 216 Xuan Thuy Street. (Cô ấy sống tại 216 đường Xuân Thuỷ.)
- “At” chỉ nơi công tác, học tập, làm việc (at work, at school…)
E.g. I will be at school from 8 a.m. to 4 p.m. tomorrow. (Tôi sẽ ở trường từ 8 giờ
sáng đến 4 giờ chiều ngày mai.)
Above
(ở phía trên)
- Diễn tả vị trí ở phía trên nhưng không ếp xúc trực ếp với vật như “on”.
E.g. There is a clock above the table. (Có một cái đồng hồ ở trên cải bàn.) Ở đây
là đồng hồ treo bên trên chứ không nằm trên mặt bàn.
- Diễn tả vị trí bên trên trong cuộc thi hoặc danh sách.
E.g. He came second in the speaking contest. Anna was above him. (Anh ta xếp
thứ 2 trong cuộc thi hùng biện. Anna ở vị trí trên anh ấy.)
Among
(ở giữa)
- “Among” mang nghĩa ở giữa trong số nhiều vật.
E.g. I found the leer among his books. (Tôi m thấy bức thư trong đống sách
của anh ấy.)
Among the ve boys, Tom is the most intelligent. (Trong số 5 bạn nam, Tom là
người thông minh nhất.)
Between
(Ở giữa)
- “Between” diễn tả vị trí nằm giữa 2 vật.
E.g. The sofa is between the lamp and the tree. (Sofa ở giữa cái đèn và cái cây.)
Behind
(phía sau)
- “Behind” diễn tả vị trí ở phía sau.
E.g. The cat is behind the TV. (Con mèo đang ở phía sau TV.)
In front of
(ở phía trước)
- “In front of’ diễn tả vị trí ở phía trước.
E.g. He is standing in front of me. (Anh ta đang đứng phía trước tôi.)
Under
(bên dưói)
- “Under” chỉ vị trí bên dưới một đồ vật.
E.g. The cat is under the sofa. (Con mèo đang ở bên dưới cái sofa.)
Next to
- “Next to” chỉ vị trí bên cạnh.
(ở cạnh)
E.g. She sat next to me during the test. (Cô ấy đã ngồi cạnh tôi suốt giờ kiểm tra.)
Near (ở gần)
- “Near” chỉ vị trí ở gần.
E.g. My school is near my house. (Trường học gần nhà của tôi.)
Opposite
(đối diện)
- “Opposite” chỉ vị trí đối diện.
E.g. The post oce is opposite my school. (Bưu điện ở đối diện trường học của
tôi.)
2. POSSESSIVE PRONOUNS- ĐẠI TỪ SỞ HỮU
2.1. Định nghĩa
Đại từ sở hữu (possessive pronouns) là những từ được sử dụng để chỉ sở hữu hoặc quan hệ giữa
người nói hoặc người viết với các vật thể, người hoặc động vật khác trong câu. Đại từ sở hữu thường
được dùng thay thế cho nh từ sở hữu và danh từ để tránh lặp. (Đại từ sở hữu = Tính từ sở hữu +
danh từ.)
E.g. l. That book is mine. (Mine = my book) (Cuốn sách đó là của tôi.)
E.g. 2. Is this umbrella yours? (Yours = your umbrella) (Cái ô này của bạn phải không?)
E.g.3. His car is parked outside. Mine is parked inside. (Mine = My car) (Xe của anh ấy đỗ ở ngoài. Xe
của tôi đỗ bên trong.)
E.g.4. Their house is on the comer. Ours is opposite. (Ours = our house) (Ngôi nhà của họ ở góc
đường. Nhà của chúng tôi thì đối diện.)
Subject pronouns
(Đại từ nhân xưng chủ ngữ)
Possessive adjecve
(Tính từ sở hữu)
Possessive pronouns
(Đại từ sở hữu)
I
my
mine
You
your
yours
We
our
ours
They
their
theirs
He
his
his
She
her
hers
It
its
its
2.2. Chức năng của đại từ sở hữu
* Đại từ sở hữu làm chủ ngữ
E.g. His car is cheap. Mine is much more expensive. (Xe của anh ta rẻ. Xe của tôi đắt hơn nhiều.)

* Đại từ sở hữu làm tân ngữ
E.g. John bought his car last month. I bought mine 2 years ago. (John mua ô tô của anh ấy tháng
trước. Tôi mua ô tô của tôi 2 năm trước.)
* Đại từ sở hữu làm tân ngữ của giới từ
E.g. I could deal with her trouble, but I don’t know what to do with mine. (Tôi có thể giải quyết khó
khăn của cô ấy, nhưng tôi không biết phải làm gì với khó khăn của mình.)
D. PRONUNCIATION
* Stress in words ending in -ese and -ee (trọng âm với những từ có hậu tố “-ese” và “-ee”)
- Những từ có hậu tố “-ese”:
Một số danh từ thường là chỉ quốc tịch, được hình thành bằng cách thêm đuôi -ese vào sau danh từ
riêng chỉ tên quốc gia đó. Các danh từ hoặc nh từ có đuôi -ese thường có trọng âm rơi vào chính nó.
E.g.
Danh từ gốc
Danh từ đuôi -ese
Japan
/dʒəˈpæn/
nước Nhật Bản
Japanese
/ˌdʒæpəˈniːz/
người Nhật Bản
China
/ˈtʃaɪnə/
nước Trung Quốc
Chinese
/ˌtʃaɪˈniːz/
người Trung Quốc
Portugal
/ˈpɔːrtʃʊɡl/
nước Bồ Đào Nha
Portuguese
/ˌpɔːrtʃʊˈɡiːz/
người Bồ Đào Nha
- Những từ có hậu tố “-ee”:
Một số danh từ thường chỉ người được hình thành bằng cách thêm đuôi -ee vào sau các động từ. Các
danh từ có đuôi -ee thường có trọng âm rơi vào chính nó.
E.g.
Danh từ gốc
Danh từ đuôi -ese
train
/treɪn/
đào tạo
trainee
/ˌtreɪˈniː/
thực tập sinh
interview
/ˈɪntəvjuː/
phỏng vấn
interviewee
/ˌɪntərvjuːˈiː/
người được phỏng vấn
examine
/ɪɡˈzæmɪn/
kiểm tra
examinee
/ɪɡˌzæmɪˈniː/
thí sinh
E. PRACTICE
Exercise 1. Choose the leer A, B, C or D to indicate the word whose underlined part diers from the
other three in pronunciaon in each of the following quesons.
1. A. language
B. cultural
C. interact
D. landline
2. A. mulmedia
B. landline
C. video
D. communicate
3. A. cultural
B. music
C. fuel
D. communicave
4. A. mulmedia
B. cultural
C. chat
D. smart
5. A. cyber
B. typhoon
C. dry
D. funny
6. A. conference
B. nonverbal
C. coee
D. body
7. A. telepathy
B. conference
C. interact
D. verbal
Exercise 2. Choose the leer A, B, C, or D to indicate the word that has a dierent stress paern
from others.
1. A. social
B. video
C. media
D. trainee
2. A. Portuguese
B. Chinese
C. Vietnamese
D. Japanese
3. A. agree
B. employee
C. aendee
D. commiee
4. A. Lebanese
B. refugee
C. guarantee
D. coee
5. A. equipment
B. examine
C. verbal
D. trainee
6. A. talkave
B. Vietnamese
C. negave
D. posive
7. A. conference
B. situaon
C. opportunity
D. interact
8. A. cultural
B. media
C. Japanese
D. dierence
Exercise 3. Choose the correct answer A, B, C or D to complete these sentences below.
1. We took part in a lot of interesng ______________ to make acquaintance with each other in the
chat room.
A. communies B. acvies C. conferences D. contests
2. The sign language provides the deaf more ______________ to communicate with those who are
deaf or hard of hearing.
A. opons B. opportunies C. situaons D. acvies
3. In a presentaon, presenters should use their body language such as hand gestures, eye contact to
communicate with the audience ______________.
A. eecve B. eecvely C. more eecve D. more eecvely
4. Nowadays, our country creates more ______________ products to persuade customers from other
countries to buy.
A. compeve B. expensive C. luxurious D. beauful
5. Try to think ______________ about troubles that you may get into in your life.
A. negave B. posive C. negavely D. posively
6. The portable wireless devices or eReaders will be paper thin, exible and have wireless __________
in the future.
A. usages B. connecons C. Wi-Fi D. techniques
7. Recent advancements in 3D imaging and scanning technologies are making your “virtual presence”
a real ______________.
A. possibility B. creavity C. quality D. identy
8. The future will bring a slew of new products that will change the way we ______________ with
each other and with machines.
A. communicated B. communicang C. communicaon D. communicate
9. Which one is not correct to ll in the blank?
Hand gestures are a type of ______________ which makes people listen to you.
A. verbal communicaon B. body language
C. sign language D. non-verbal communicaon
10. With mobile ______________, devices with solar power can be put in relavely remote locaons,
or can be free to roam.
A. phones B. connecvity C. vehicles D. equipment
Exercise 4. Match the words with the denions
1. chat room
A. An online discussion group in which you can leave message or post
quesons
2. mulmedia
B. A phone that uses a telephone line for transmission
3. landline phone
C. A device with a touch screen with funcon similar to computer, a
digital camera, and a GPS device, in addion to a phone
4. smart phone
D. People join this Internet area to communicate online. The
conversaons are sent immediately and are visible to everyone there
5. message board
E. Mulple forms of communicaon on a computer including sounds,
videos, video-conferencing, graphics, and texts
Answer:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Exercise 5. Fill in the blank with the words from the box to complete the sentences.
facial expressions
emails
face-to-face meeng
leers

body language
texng
video chat
signs
1. Teenagers oen use abbreviaons when ______________ to save me.
2. People who cannot hear or speak oen communicate with each other by using ______________.
3. In a ______________, people communicate directly to each other.
4. Using ______________ during your talk is an eecve way to aract more people’s aenon.
5. In the past, people who live far away used to write ______________ to keep in touch with their
relaves or their family.
6. ______________ helps people connect to each other in such a quick and cheap way.
7. Smiling and blinking your eyes are examples of ______________.
8. Since the appearance of the Internet, people have been able to send ______________ to contact
people from any country in the world.
Exercise 6. Choose the correct opons to complete these sentences below.
1. The children are playing ______________.
A. out B. outside C. at D. in
2. May comes ______________ April.
A. before B. aer C. from D. against
3. There is a clock ______________ the wall in my class.
A. near B. across C. on D. at
4. Where is Susan? - She is sing ______________ Jim.
A. on B. under C. between D. next to
5. We’re studying ______________ Sai Gon University.
A. at B. in C. of D. from
6. There are 40 students ______________ the class.
A. inside B. in C. at D. over
7. My pen is ______________ the books and the computer.
A. among B. down C. up D. between
8. I saw a mouse ______________ the chair.
A. among B. between C. in D. behind
9. My house is ______________ to the hospital.
A. close B. near C. opposite D. Across
10. We come ______________ Viet Nam.
A. in B. above C. from D. below
Exercise 7. Choose the best answer A, B, C or D to complete each sentence.
1. The train leaves _____ tomorrow morning _____ 8 a.m.
2. I love going skiing _____ January.
3. We met at the restaurant _____ 8 p.m.
4. The class is _____ 9 a.m _____ Monday mornings.
5. I like to drink coee _____ the morning and tea _____ the aernoon.
6. We went out for dinner _____ last Wednesday.
7. She le London _____ the 4
th
of March.
8. I had a party _____ my birthday.
9. Lucy went to New York _____ New Year's Eve.
10. We’re meeng _____ lunchme _____ next Tuesday.
Exercise 8. Choose one suitable word from brackets to complete the sentences.
1. Is this cup _____ (your / yours)?
2. The coee is _____ (my / mine).
3. That coat is _____ (my/mine).
4. He lives in _____ (her / hers) house.
5. You might want _____ (your / yours) phone.
6. The new car is _____ (their / theirs).
7. She cooked _____ (our / ours) food.
8. Don’t stand on _____ (my / mine) foot!
9. She gave him _____ (her / hers) suitcase.
10. I met _____ (their / theirs) mother.
11. Is this _____ (their / theirs) coee?
12. Is the at _____ (her / hers)?
13. The gray scarf is _____ (my / mine).
14. That red bike is _____ (our / ours).
15. We should take _____ (our / ours) coats.
16. That is _____ (my / mine) car.
17. He dropped _____ (my / mine) bag.
18. Are these phones _____ (their / theirs)?
19. These cakes are _____ (our / ours)!
20. Are those children _____ (your / yours)?
Exercise 9. Circle the correct answers.
1. Tina is _____ sister.
A. my B. mine C. I D. me
2. _____ went to the cinema yesterday.
A. Her B. Hers C. She D. Herself
3. This car is _____.
A. his B. him C. he D. himself
4. These are the children’s shoes. They’re _____.
A. their B. they C. theirs D. them
5. Look at _____!
A. my B. I C. me D. mine
6. _____ brother is tall.
A. His B. Him C. Himself D. He
7. I waited for _____ yesterday but you didn’t come.
A. your B. you C. yourself D. yours
8. These are _____ pencils.
A. ours B. we C. us D. our
9. This leer is for _____.
A. she B. hers C. her D. herself
10. _____ didn’t do the homework.
A. Yourself B. You C. Your D. Yours
11. This is John’s book. It is _____ book.
A. he B. his C. him D. himself
12. Whose bag is this? - It’s _____.
A. I B. mine C.my D. me
13. Whose jeans are these? - They’re _____.
A. his B. himself C. he D. him
14. Our car is bigger than _____.
A. they B. theirs C. them D. their
15. Whose diconary is this? - It’s _____.
A. her B. she C. hers D. herself
16. Junko has eaten her lunch already, but I’m saving _____ unl later.
A. hers B. her C. my D. mine
17. We gave them _____ telephone number, and they gave us _____.
A. ours, their B. our, their C. ours, theirs D. our, theirs
18. _____ computer is a Mac, but _____ is a PC.
A. Your, mine B. Yours, mine C. Your, my D. Yours, my
19. You can’t have any chocolate! It’s _____!
A. your B. its C. her D. mine
20. Was _____ grammar book expensive?
A. your B. yours C. your’s D. you
21. _____ pencil is broken. Can I borrow _____?
A. Mine, yours B. Your, mine C. My, yours D. Yours, mine
22. Jody has lost _____ book.
A. mine B. her C. hers D. theirs
23. This bird has broken _____ wing.
A. it’s B. its’ C. hers D. its
24. My telephone is out of order, but _____ is working.
A. your B. our C. his D. their
25. These grammar books are dierent. _____ has 278 pages, but _____ has only 275 pages.
A. Yours, mine B. Your, my C. Yours, my D. Your, min
Exercise 10. Read the passages below and choose the best tle for each passage. (There is one
unnecessary tle)
Title 1 - Why do “friends” websites seem dangerous?
Title 2 - How do “friends” websites work?
Title 3 - What’s the best advice for people who want to use “friends” websites?
Title 4 - Where do Millie’s friends live?
Title 5 - How can I nd “friends” websites?
Title 6 - Why are “friends” websites popular?
1. _______________ Millie is 14 years old and lives in Miami. She has 204 friends - and she makes two
or three more friends every week. About 20 of her friends also live in Miami. Some go to the same
school, and others go to the same music clubs and sports centers. She oen sees them. The others
live in other cies and other countries: England, Canada, Japan ... She never meets these friends, but
she talks to them on the Internet. They are her “My Space Friends”.
2. _______________ Because of websites like MySpace, Yahoo 360 and Bebo. people can make
friends online. These websites are very popular all over the world, especially with young people. Users
have their own homepage. They give informaon about themselves. They write leers for their
webpage, show photos and give opinions. They write about their favourite lms, music and TV
programmes.
3. _______________ For many young people, a good homepage is an important part of their image. It
says: “This is me! I have something to say. These things - and these people - are important in my life.”
And these websites are also an easy way to talk to a lot of dierent people. That is why teenagers like
these “friends” websites.
4. _______________ But some people are worried that these websites aren’t safe. For example, it is
impossible to know that the informaon on a homepage is true. Perhaps the 14-year-old girl you talk
to online is really a 40-year-old man.
5. _______________ So here is some advice. Keep your webpage private, (only friends can see a
private homepage). Do not put photos of yourself on your homepage. Do not meet people that you
only know because of the website. And nally, remember that online friends are fun, but they are not
the same as real friends.
Exercise 11. Read the text and answer the quesons.
SIGN LANGUAGE
Because deaf people cannot hear, they have special ways of communicang. For example, they can
learn to understand what someone is saying by looking at the mouth of the speaker. This is called lip-
reading. Also, speaking is very dicult for the deaf, because they cannot hear their own voices.
However, it is possible with special training. According to many deaf people all around the world, the
most praccal and popular way of communicang is with sign language.
In many ways, sign language is similar to spoken language. The words of sign language are made with
signs, which are formed with movements of the hands, face, and body. As with words, each sign has a
dierent meaning and can be combined to form sentences. Sign languages also have their own
grammar. The alphabet of sign language is special hand signs that stand for leers; they make spelling
possible. The signs combine to form a rich language that can express the same thoughts, feelings, and
ideas as any spoken language. And just as people from dierent countries speak dierent languages,
most countries have their own variety of sign languages.
1. How can deaf people communicate with others?
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. Why is speaking dicult for the deaf?
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. Is sign language similar to spoken language in every way?
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. How is sign language expressed?
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. What stands for leers in the alphabet of sign language?
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. Does sign language dier between countries?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 12. Read the text and answer these following quesons.
Telephones help people speak to one another when they are apart. For more than a hundred
years, nearly every telephone was a landline. A landline telephone is one that needs to be connected
by a wire to a network of other telephones. Because of the wires, people could not take those
telephones with them when they le their homes or oces.
What if you had to make a call while you were away from home? You had to nd a pay phone. Pay
phones are landlines found in public places. Many pay phones are on the street. You can make a call
from inside a glass or metal space called a phone booth. Once you are inside the booth, you put coins
into a slot in the phone to make a call.
Telephones have seen a lot of progress. Today, many people carry cell phones. Cell phones do not
need to be connected with wires. They can be used almost anywhere and can t in an adult’s hand.
Many cell phones sold today are smartphones. A smartphone is a cell phone that has lots of
computer-style features. For example, people use smartphones to check e-mail and go on the
Internet. And all that can be done using something small enough to carry in a pocket!
1. Does a landline need to be connected by a wire to a network of other telephones?
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. Why weren’t people able to take the landline with them to work?
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. What are payphones?
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. What does “they” in paragraph 3 refer to?
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. What is the dierence between a smartphone and a cell phone?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 13. Reorder the words to have correct sentences.
1. used/ conferencing/ be/ special occasions/ for/ or/ video/ short conversaons/ will/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. very/ among/ has/ social media/ people/ popular/ become/ young/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. by/ way/ is/ a/ communicate/ instantly/ thought/ telepathy/ to/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. than/ text messages/ are/ ever/ sending/ before/ more/ teens/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. by/ in/ communicang/ will/ telepathy/ people/ years/ be/ 30/?
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. to/ someone/ is/ know/ oen/ give/ a/ that/ something/ good/ we/ let/ “thumbs-up”/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
7. allows/ chang/ the/ watch/ via/ webcam/ body language/ with/ you/ to/ friends/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
8. changed/ way/ each other/ we/ has/ with/ communicate/ technology/ the/ dramacally/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
9. cell/ face-to-face/ texng/ their/ prefer/ on/ to talking/ today/ teenagers/ phones/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
10. help/ of/ barrier/ with/ communicate/ the/ language/ spite/ can/ foreigners/ in/ gestures/.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 14. Write the second sentence so that it has the same meaning to the rst one.
1. They will provide 5G in certain areas of the city, won’t they?
→ Will 5G
2. Beck had diculty understanding her daughter’s text messages.
→ Beck found it
3. Video conferencing technology allows people in remote places to hold face-to- face meengs.
→ Video conferencing technology lets
4. The rst me that I created an email account is sll unforgeable.
→ I sll remember
5. Making a video call without the network is impossible.
→ It’s
6. Face-to-face communicaon is beer than texng.
→ Texng isn’t
7. Could you please conrm the date and me of the meeng?
→ Would you
8. The teacher made me stay in aer school and do extra work.
→ I
9. ‘Why don’t we give Jean a video call?’ Albert said.
→ Albert suggested
10. My mother does her shopping at about this me every week.
→ This me next week my mother
Exercise 15. Currently, two popular forms of communicaon are face-to-face communicaon and
online communicaon. State the posives and negaves of these two types of communicaon.
Face-to-face communicaon
Online communicaon
Posive
Negave

Exercise 16. The COVID-19 pandemic has forced global communicaon to take place online. From
the posives and negaves of this form of communicaon, write a paragraph about the future form
of online communicaon. (About 150 words)
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
UNIT 11. SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A. VOCABULARY
WORD
PRONNCIATION
MEANING
applicaon (n)
/ˌæplɪˈkeɪʃn/
ứng dụng
E.g. What are the praccal applicaons of this invenon? Các ứng dụng thực tế của phát minh này
là gì?
aendance (n)
/əˈtendəns/
sự có mặt, sĩ số
E.g. Teachers must keep a record of students’ aendances. Giáo viên phải lưu giữ một bản ghi chép
kiểm tra sĩ số học sinh.
biometric (adj)
/ˌbaɪəʊˈmetrɪk/
thuộc về sinh trắc
E.g. The major biometric methods include face, voice, ngerprint and iris. Các phương pháp sinh
trắc học chính bao gồm khuôn mặt, giọng nói, dấu vân tay và tròng mắt.
breakout room (n)
/ˈbreɪkaʊt ruːm/
phòng học chia nhỏ, chia nhóm
E.g. The online conference has set up breakout rooms to discuss soluons for the air polluon. Hội
nghị trực tuyến đã bố trí các phòng họp nhóm đế thảo luận các giải pháp khắc phục nh trạng ô
nhiễm không khí.
cheang (n)
/tʃiːt ɪŋ/
sự lừa dối, gian dối, gian lận
E.g. His cheang on the nal examinaon queered his chances of graduaon. Việc anh ấy gian lận
trong kỳ thi cuối kỳ đã làm mất đi cơ hội tốt nghiệp của anh ấy.
complain (v)
/kəmˈpleɪn/
phàn nàn, khiếu nại
E.g. She never complains, but she’s obviously exhausted. Cô ấy không bao giờ phàn nàn, nhưng cô
ấy rõ ràng là kiệt sức.
contact lens (n)
/ˈkɒntækt lenz/
kính áp tròng
E.g. She takes out her contact lens. Cô ấy thảo kính áp tròng ra.
convenient (adj)
/kənˈviːniənt/
thuận ện, ện lợi
E.g. A bicycle is oen more convenient than a car in a big city. Một chiếc xe đạp thường thuận ện
hơn một chiếc ô tô trong thành phố lớn.
develop (v)
/dɪˈveləp/
phát triển, triển khai
E.g. Some children develop more slowly than others. Một số trẻ phát triển chậm hơn những trẻ
khác.
digital (adj)
/ˈdɪdʒɪtl/
số, kĩ thuật số
E.g. Adversers are pung more and more money into digital markeng. Các nhà quảng cáo đang
đầu tư ngày càng nhiều ền vào ếp thị kỹ thuật số.
discover (v)
/dɪˈskʌvər/
phát hiện, khám phá
E.g. Sciensts around the world are working to discover a cure for AIDS. Các nhà khoa học trên
khắp thế giới đang làm việc để m ra phương pháp chữa trị bệnh AIDS.
epidemic (n)
/ˌepɪˈdemɪk/
dịch bệnh
E.g. An epidemic of measles broke out, and over 200 children died. Dịch sởi bùng phát, hơn 200 trẻ
em tử vong.
experiment (n)
/ɪkˈsperɪmənt/
thí nghiệm
E.g. Many people do not like the idea of experiments on animals. Nhiều người không thích ý tưởng
thí nghiệm trên động vật.
eye-tracking
/’aɪ trækɪŋ/
theo dõi (cử động) mắt
E.g. We use eye-tracking equipment in our labs. Chúng tôi sử dụng thiết bị theo dõi ánh mắt trong
phòng thí nghiệm của mình.
face-to-face (adj)
/ˌfeɪs tə ˈfeɪs/
trực ếp, mặt đối mặt
E.g. I deal with customers on the phone and rarely meet them face-to-face. Tôi giao dịch với khách
hàng qua điện thoại và hiếm khi gặp mặt trực ếp.
feedback (n)
/ˈːdbæk/
(ý kiến) phản hồi, hồi đáp
E.g. I’ve heard loads of good feedback about this product. Tôi đã nghe rất nhiều phản hồi tốt về sản
phẩm này.
ngerprint (n)
/ˈfɪŋɡərprɪnt/
(dấu) vân tay
E.g. She was careful not to leave any ngerprints. Cô ta cẩn thận không để lại bất kỳ dấu vân tay
nào.
invent (v)
/ɪnˈvent/
phát minh
E.g. Louis Braille invented an alphabet to help blind people. Louis Braille đã phát minh ra bảng chữ
cái để giúp người mù.
invenon (n)
/ɪnˈvenʃn/
sự phát minh, sáng chế
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm
E.g. The Internet is a great invenon of the mes. Internet là một phát minh vĩ đại của thời đại.
mark (v)
/mɑːrk/
chấm điểm
E.g. The teacher marked her lesson yesterday. Giáo viên đã chấm bài của cô ấy ngày hôm qua.
plaorm (n)
/ˈplæɔːrm/
nền tảng, bục, bệ, sân ga
E.g. She used the newspaper as a plaorm for her view. Cô ấy đã sử dụng báo chí làm nền tảng cho
quan điểm của mình.
recognion (n)
/ˌrekəɡˈnɪʃn/
sự nhận biết, sự công nhận
E.g. The scienst deserves recognion for his talent. Nhà khoa học xứng đáng được công nhận tài
năng của mình.
scanner (n)
/ˈskænər/
máy quét
E.g. The picture is digized by a scanner. Hình ảnh được số hóa bằng máy quét.
science (n)
/ˈsaɪəns/
khoa học
E.g. Meteorology is the science of the weather. Khí tượng học là khoa học về thời ết.
screen (n)
/skriːn/
màn hình, màn chiếu
E.g. The screen suddenly went fuzzy. Màn hình đột nhiên mờ đi.
soluon (n)
/səˈluːʃn
giải pháp, đáp án
E.g. Aempts to nd a soluon have failed. Những nỗ lực để m giải pháp đều thất bại.
technology (n)
/tekˈnɒlədʒi/
công nghệ
E.g. This technology enables computers to read handwring. Công nghệ này giúp cho máy nh đọc
được chữ viết tay.
truancy (n)
/ˈtruːənsi/
trốn học, nghỉ học không phép
E.g. Truancy rates at this high school are very high. Tỷ lệ trốn học ở trường trung học này rất cao.
B. WORD FORMATION
Word
Related words
Transcripon
Meaning
archaeology (n)
/ˌɑːkiˈɒlədʒi/
khảo cổ học
archaeological (adj)
/ˌɑːkiəˈlɒdʒɪkl/
thuộc về khảo cổ học
archaeologist (n)
/ˌɑːkiˈɒlədʒɪst/
nhà khảo cổ học
benet (n, v)
/ˈbenɪfɪt/
lợi ích, hưởng lợi
benecial (adj)
/ˌbenɪˈfɪʃl/
có lợi ích, hữu ích
benecent (n)
/bɪˈnefɪsnt/
hay làm phúc, làm việc thiện
cure (n, v)
/kjʊər/
chữa khỏi
curable (adj)
/ˈkjʊərəbl/
có thể chữa khỏi
discover (v)
/dɪˈskʌvər/
phát hiện ra, khám phá ra
discovery (n)
/dɪˈskʌvəri/
sự khám phá, sự phát hiện
ra
discoverable (adj)
/dɪˈskʌvərəbl/
có thể khám phá, có thể m
ra
explore (v)
/ɪkˈsplɔːr/
khám phá, thám hiểm
exploraon (n)
/ˌekspləˈreɪʃn/
sự khám phá, sự thám hiểm
explorave (adj)
/ɪkˈsplɔːrətɪv/
có nh chất thăm dò, có nh
thám hiểm
exploratory (adj)
/ɪkˈsplɒrətri/
có nh chất thăm dò, có nh
thám hiểm
explorer (n)
/ɪkˈsplɔːrər/
người thám hiểm
improve (v)
/ɪm'pru:v/
nâng cao, cải thiện
improvement (n)
/ɪm'pru:vmənt/
sự cải thiện, ến bộ
invent (v)
/ɪn'vent/
phát minh, sáng chế
invenon (n)
/ɪn'venʃn/
sự phát minh, sáng chế
inventor (n)
/ɪn'ventər/
nhà phát minh
invenve (adj)
/ɪn'ventɪv/
có tài phát minh, có tài sáng
chế
support (v)
/səˈpɔːrt/
ủng hộ
supporter (n)
/səˈpɔːrtər/
người ủng hộ
supporve (adj)
/səˈpɔːrtɪv/
mang lại sự giúp đỡ
supporng (adj)
/səˈpɔːrtɪŋ/
phụ, chống, đỡ
technique (n)
/tekˈniːk/
thuộc về kĩ thuật
technical (adj)
/ˈteknɪkl/
kĩ thuật, công nghệ
technology (n)
/tekˈnɒlədʒi/
thuộc công nghệ
technological (adj)
/ˌteknəˈlɒdʒɪkl/
có nh chất kỳ thuật
technologically (adv)
/ˌteknəˈlɒdʒɪkli/
thuộc về kĩ thuật
science (n)
/ˈsaɪəns/
khoa học
scienc (adj)
/ˌsaɪənˈtɪfɪk/
thuộc về khoa học
scienst (n)
/ˈsaɪəntɪst/
nhà khoa học
transform (v)
trænsˈfɔːrm/
chuyển đổi, biến đổi
transformaon (n)
/ˌtrænsfərˈmeɪʃn/
sự chuyển đổi, sự biến đổi
transformer (n)
/trænsˈfɔːrmər/
người làm biến đổi
C. GRAMMAR
Reported speech (statement) – Lời nói gián ếp (câu trần thuật)
1. Phân biệt lời nói trực ếp và lời nói gián ếp.
a. Lời nói trực ếp, là sự lặp lại chính xác những từ của người nói. Lời nói trực ếp được đặt trong
dấu ngoặc kép và sau động từ chính có dấu phẩy (,) hoặc dấu hai chấm (:).
- Đôi khi mệnh đề chính cũng có thể đặt sau lời nói trực ếp.
E.g. “I don’t like this party.” Bill said.
b. Lời nói gián ếp (indirect/reported speech) là lời tường thuật lại ý của người nói, đôi khi không cần
phải sử dụng chính xác những từ của người nói.
E.g. Bill said that he didn’t like that party.
2. Quy tắc chuyển đổi từ câu trực ếp sang câu gián ếp
Để chuyển một câu từ trực ếp sang gián ếp chúng ta phải ến hành một số biến đổi sau:
Bước 1: Thay đổi về đại từ nhân xưng, đại từ sở hữu, nh từ sở hữu:
Chủ ngữ
Trực ếp
Gián ếp
I
he, she
we
they
You
they/ he/ she/I
Tân ngữ
Trực ếp
Gián ếp
me
him/ her
us
them
you
them/ him/ her
Tính từ sở hữu
Trực ếp
Gián ếp
my
his/ her
our
their
your
their/ his/her/ my
Đại từ sở hữu
Trực ếp
Gián ếp
mine
his / hers
ours
theirs
yours
theirs/ his/ hers
Bước 2: Thay đổi động từ: Thì của các động từ trong lời nói gián ếp phải LÙI MỘT THÌ so với câu trực
ếp. Dưới đây là bảng quy tắc lùi thì.
Trực ếp
Gián ếp
1. Present Simple: V1
E.g. Nam said “I am told to be at school before 7
o’clock.”
E.g. He said “I like beer.”
1. Past Simple: V2/ed
E.g. Nam said (that) he was told to be at school
before 7 o’clock.
E.g. He said (that) he liked beer.
2. Present Progressive: am/is/are + V-ing
E.g. He said “I’m watching TV.”
2. Past Progressive: was/were + V-ing
E.g. He said (that) he was watching TV.
3. Present Perfect: has/have + V3/ed
E.g. He said “I have just bought a new book”.
3. Past Perfect: had + V3/ed
E.g. He said (that) he had just bought a new
book.
4. Past Simple: V2/ed
E.g. They said “We came by car”.
4. Past Perfect: had + V3/ed
E.g. They said (that) they had come by car.
5. Past Progressive: was/were + V-ing
E.g. He said “I was sing in the park at 8
o’clock”.
5. Past Progressive or Past Perfect progressive
E.g. He said (that) he was sing in the park at 8
o’clock”.
He said (that) he had been sing in the park at 8
o’clock”.
6. Past Perfect: had + V3/ed
6. Past Perfect: had + V3/ed
E.g. She said “My money had run out”.
E.g. She said (that) her money had run out.
7. Future Simple: will + V
E.g. Lan said “I’ll phone you”.
7. Future in the past: would + V
E.g. Lan said (that) she would phone me.
8. can
E.g. He said “You can sit here”.
8. could
E.g. He said (that) we could sit there.
9. may
E.g. Mary said “I may go to Ha Noi again”.
9. might
E.g. Mary said (that) she might go to Ha Noi
again.
10. must/ have to
E.g. He said “I must nish this report”.
10. had to
E.g. He said (that) he had to nish that report.
* Chú ý: Một số trường hợp không đổi thì của động từ trong câu gián ếp:
- Nếu động từ ở mệnh đề giới thiệu được dùng ở thì hiện tại đơn, hiện tại ếp diễn, hiện tại hoàn
thành hoặc tương lai đơn, thì của động từ trong câu gián ếp vẫn không thay đổi
E.g. He says/ he is saying/ he has said/ he will say, “the text is dicult”.
→ He says/ is saying/ has said/ will say (that) the text is dicult.
- Khi câu nói trực ếp thể hiện một chân lý hoặc một hành động lặp lại thường xuyên, thì của động từ
trong câu gián ếp vẫn không thay đổi
E.g. My teacher said “The Sun rises in the East”.
→ My teacher said (that) the Sun rises in the East.
He said, ‘My father always drinks coee aer dinner’.
→ He said (that) his father always drinks coee aer dinner.
- Nếu lúc tường thuật, điểm thời gian được đưa ra trong lời nói gián ếp vẫn chưa qua, thì của động
từ và trạng từ thời gian vẫn được giữ nguyên
E.g. He said, “I will come to your house tomorrow”.
→ He said (that) he will come to my house tomorrow.
- Câu trực ếp có dạng câu điều kiện loại 2 hoặc loại 3:
E.g. He said, “If I knew her address, I would write to her”.
→ He said that he would write to her if he knew her address .
E.g. She said, “If I had enough money, I would buy a new bicycle.”
→ She said (that) if she had enough money, she would buy a new bicycle.
E.g. The teacher said, “If John had studied harder, he wouldn’t have failed his exam.”

→ The teacher said (that) if John had studied harder, he wouldn’t have failed his exam.
- Tuy nhiên nếu lời nói trực ếp là câu điều kiện loại 1 thì được chuyển sang loại 2 ở lời nói gián ếp.
E.g. The adversement said, “If you answer the quesons correctly, you may win one million dollars”.
→ The adversement said that I might win one million dollars if I answered the quesons correctly.
- Không thay đổi thì của mệnh đề sau “wish”
E.g. He said, “I wish I had a lot of money”.
→ He wishes (that) he had a lot of money.
- Không thay đổi thì của mệnh đề sau "It s (high/ about) me”
E.g. She said, “It’s about me you went to bed, children”.
→ She told her children that it’s about me they went to bed.
- Không thay đổi thì của mệnh đề đi sau "would rather, would sooner”
E.g. She said, “I would rather you stayed at home”.
→ She said that she would rather I stayed at home.
- Không thay đổi thì của:
Could, would, might, should, ought to, had beer, need trong câu nói gián ếp
Nhưng must → had to/ must
E.g. She said, “I could do the homework.”
→ She said that she could do the homework.
- Động từ trong câu nói trực ếp có thời gian xác định:
E.g. He said, “I was bom in 1980”.
→ He said that he was bom in 1980.
- Mệnh đề trạng ngữ chỉ thời gian trong câu phức có thì quá khứ đơn và quá khứ ếp diễn
E.g. “I saw him when he was going to the cinema”.
→ She said she saw him when she was going to the cinema.
Bước 3: Thay đổi về từ chỉ thời gian và nơi chốn:
Trực ếp
Gián ếp
today/ tonight
that day/ that night
yesterday
the day before/ the previous day
last month/ night...
the month before / the previous month/ the night before/ the
previous night
tomorrow
the following day/ the next day
this month
that month
the day before yesterday
two days before
the day aer tomorrow
in two days’ me
next month
the month aer / the following month
here
there
now
then
ago
before
this
that
these
those
1.3. Statements in reported speech (Câu trần thuật trong lời nói gián ếp)
Để chuyển một câu trần thuật trực ếp sang lời nói gián ếp ta ến hành 3 bước như đã nêu ở trên.
Chú ý: động từ dẫn trong câu trần thuật sẽ là: said, told, announced, explained...
Cấu trúc: S + said (to + O)/ told + O that S’ + V (lùi thì)
E.g. “We will have a test tomorrow”, my teacher said.
→ My teacher said (that) they would have a test the next day. (chuyển We
→
they, tomorrow —> the
next day, và động từ ở thì tươmg lai đơn will have
→
would have)
E.g. “I’m going to study abroad next year”, she said.
→ She said that she was going to study abroad the following year, (đổi I
→
she, động từ am going to
→
was going to, next year
→
the following year)
D. PRONUNCIATION
SENTENCE STRESS - TRỌNG ÂM CÂU
- Trọng âm của câu là một yếu tố rất quan trọng trong khi nói ếng Anh, nó tạo nên ngữ điệu của câu
và đôi khi còn thể hiện ẩn ý của người nói. Trọng âm của câu thường được nhấn vào các từ khoá hay
từ mang nội dung chính (content words).
E.g. We visited a famous cra village in Ha Noi. (Chúng tớ đã đến thăm một làng nghề thủ công nổi
ếng ở Hà Nội.)
Trong văn nói thì các loại từ dưới đây sẽ thường được nhấn trọng âm vào.
Từ mang nội dung chính trong câu
Ví dụ
Động từ
sell, give, employ
Danh từ
car, music, table
Tính từ
red, small, beauful
Trạng từ
quickly, never, why
Trợ từ phủ định
don’t, aren’t, can’t
Đáp án trong câu hỏi dạng đảo
yes, no
Không nhấn trọng âm vào các từ sau
Từ cấu trúc
Ví dụ
Đại từ
he, we, they
Giới từ
on, at, into
Mạo từ
a, an, the
Liên từ
and, but, because
Trợ động từ
do, be, have, can, must
E. PRACTICE
Exercise 1. Underline the stressed words in each of the following sentences.
1. The life cycle of salmon is a closed cycle.
2. It is necessary to protect forests.
3. They made their living by catching sh in the ocean every day.
4. It isn’t easy to leave here aer such a long me.
5. She is good at Math; besides, she can speak 5 languages uently.
6. The Japanese eat healthily, so they live for a long me.
7. The Americans oen eat fast food, so many of them are overweight.
8. In spring, there are various fesvals throughout the country.
9. She never eats junk food because it’s bad for her health.
10. I prefer going to the cinema.
Exercise 2. Read the sentences in exercise 1 aloud and emphasize the stressed words.
Exercise 3. What are the names of these invenons?

1. ________________
2. ________________
3. ________________
4. ________________
5. ________________
6. ________________
7. ________________
8. ________________
Exercise 4. Choose the correct opon to complete each sentence.
1. Generally speaking, most technology has had a ________________ eect on our lives.
A. benet B. benece C. benecial D. benecent
2. It remains to be seen what the ________________ impact of this technology will be.
A. long B. long-term C. boring D. relax
3. Few ________________ have had a greater inuence on mankind than the computer.
A. invent B. inventors C. invenons D. invenng
4. It is undeniable that ________________ have revoluonized our lives.
A. computers B. computer C. computerizing D. computed
5. The 21
st
century has already seen considerable ________________ in computer technology.
A. progress B. progressing C. progresses D. process
6. It is not easy to predict how this ________________ is going to develop.
A. technique B. technology C. technologies D. technologizing
7. One major ________________ in the use of computers is transport regulaon.
A. advance B. advances C. advanced D. advantage
8. The cloud is one of the latest ________________ in computer technology.
A. innovate B. innovaon C. innovaons D. innovang
Exercise 5. Match the names of occupaons with their denions.
1. chemist
a. a person who has invented something.
2. archaeologist
b. a person who travels to unknow places in orders to nd out what is
there.
3. soware developer
c. a person who works to protect the environment, plants, animals and
natural resources.
4. physicist
d. a person who studies the buildings, graves, tools, and other objects
of people who lived in the past.
5. explorer
e. a person who builds and creates Computer programs.
6. biologist
f. a scienst who works with Chemicals or studies their reacons.
7. inventor
g. a scienst who studies Physics.
8. conservaonist
h. a scienst who studies living things.
Answer:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Exercise 6. Complete the sentences with the words in exercise 5.
1. Christopher Columbus was an Italian ________________ who discovered the Americas.
2. Marie Curie was a Polish ________________ who discovered the elements polonium and radium.
3. The ________________ reconstructed the broken ancient vase from its fragments.
4. As a ________________, you’ll work to protect and enhance the local environment.
5. Mr. Kaku is a quantum ________________, a founder of string eld theory.
6. Ma works as a ________________ for a computer manufacturer.
7. Eugenie Clark was an American marine ________________ who worked with sharks.
8. Tim Berners-Lee is best known as the ________________ of the World Wide Web.
Exercise 7. Complete the table and mark the main stress on each word. Number 1 has been done for
you as an example.
Verb
Noun
invent
1. invenon
develop
2. ________________
3. ________________
advance
improve
4. ________________
5. ________________
analysis
6. ________________
arrangement
Exercise 8. Choose the best answers.
1. Charlie said, “I’m thinking of going to live in Canada”.
A. Charlie said that I was thinking of going to live in Canada.
B. Charlie said that I am thinking of going to live in Canada.
C. Charlie said that he was thinking of going to live in Canada.
D. Charlie said that he is thinking of going to live in Canada.
2. Charlie said, “My father is in hospital”.
A. Charlie said that my father is in hospital.
B. Charlie said that his father was in hospital.
C. Charlie said that his father is in hospital.
D. Charlie said that my father was in hospital.
3. Charlie said, “Nora and Jim are geng married tomorrow”.
A. Charlie said that Nora and Jim are geng married tomorrow.
B. Charlie said that Nora and Jim were geng married the next day.
C. Charlie said that Nora and Jim were geng married tomorrow.
D. Charlie said that Nora and Jim are geng married the next day.
4. Charlie said, “I haven’t seen Bill for a while”.
A. Charlie said that he hadn’t seen Bill for a while.
B. Charlie said that I haven’t seen Bill for a while.
C. Charlie said that he hasn’t seen Bill for a while.
D. Charlie said that I hadn’t seen Bill for a while.
5. Charlie said, “I’ve been playing tennis recently”.
A. Charlie said that I’ve been playing tennis recently.
B. Charlie said that he had been playing tennis recently.
C. Charlie said that he had bee playing tennis recently.
D. Charlie said that I had been playing tennis recently.
6. Charlie said. “Margaret has had a baby”.
A. Charlie said Margaret has had a baby.
B. Charlie said Margaret had had a baby.
C. Charlie said Margaret had a baby.
D. Charlie said Margaret has a baby.
7. Charlie said, “I don’t know what Fred is doing”.
A. Charlie said that he doesn’t know what Fred is doing.
B. Charlie said that he didn’t know what Fred is doing.
C. Charlie said that he doesn’t know what Fred was doing.
D. Charlie said that he didn’t know what Fred was doing.
8. Charlie said, “I hardly ever go out these days”.
A. Charlie said that he hardly ever went out these days.
B. Charlie said that I hardly ever go out these days.
C. Charlie said that I hardly ever went out these days.
D. Charlie said that he hardly ever goes out these days.
9. Charlie said, “I work 14 hours a day”.
A. Charlie said that he works 14 hours a day.
B. Charlie said that he worked 14 hours a day.
C. Charlie said that I work 14 hours a day.
D. Charlie said that I worked 14 hours a day.
10. Charlie said, “I’ll tell Jim I saw you”.
A. Charlie said he’ll tell Jim he saw me.
B. Charlie said I would tell Jim I had seen you.
C. Charlie said he would tell Jim he had seen me.
D. Charlie said I would tell Jim he had seen me.
11. Charlie said, “You can come and stay with me if you are ever in London”.
A. Charlie said you could come and stay with him if you were ever in London.
B. Charlie said I could come and stay with him if I were ever in London.
C. Charlie said you can come and stay with him if you are ever in London.
D. Charlie said I can come and stay with him if I am ever in London.
12. Charlie said, “Tom had an accident last week but he wasn’t injured”.
A. Charlie said Tom had an accident last week but he wasn’t injured.
B. Charlie said Tom had had an accident last week but he wasn’t injured.
C. Charlie said Tom had had an accident the previous week but he hadn’t been injured.
D. Charlie said Tom had an accident last week but he hadn’t been injured.
13. Charlie said, “I saw Jack at a party a few months ago and he seemed ne”.
A. Charlie said he had seen Jack at a party a few months ago and he had seemed ne.
B. Charlie said I saw Jack at a party a few months ago and he seemed ne.
C. Charlie said he had seen Jack at a party a few months ago and he seemed ne.
D. Charlie said he saw Jack at a party a few months ago and he had seemed ne.
14. Tom said, “New York is bigger than London”.
A. Tom said that New York was bigger than London.
B. Tom says that New York is bigger than London.
C. Tom says that New York was bigger than London.
D. Tom said that New York is bigger than London.
15. “Stay in bed for a few days”, the doctor said to me.
A. The doctor told me stay in bed for a few a days.
B. The doctor told to me to stay in bed for a few days.
C. The doctor said me to stay in bed for a few days.
D. The doctor told me to stay in bed for a few days.
Exercise 9. Choose the correct answers.
1. Mary: “I love chocolate.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ chocolate.”
a. loved b. loves c. loving
2. Mary: “I went skiing.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ skiing.”
a. went b. had gone c. have gone
3. Mary: “I will eat steak for dinner.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ eat steak for dinner.”
a. willing b. will c. would
4. Mary: “I have been to Sydney.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ to Sydney.”
a. had been b. has been c. was being
5. Mary: “I have had three cars.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ three cars.”
a. has b. has had c. had had
6. Mary: “I’m going to go to Long Beach.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ going to go to Long
Beach.”
a. is b. was c. went
7. Mary: “I don’t like spinach.” Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ like spinach.”
a. doesn’t b. don’t c. didn’t
8. Mary: “I have never been to London.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ never been to
London.”
a. had b. has c. have
9. Mary: “I was swimming.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ swimming.”
a. has been b. had been c. have been
10. Mary: “I had a cat.” - Jill: “Mary said (that) she _________ a cat.”
a. have b. has c. had
Exercise 10: Turn into the reported speech.
1. “I will never see you again,” the boy said to the girl.
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. He said to her, “You are my best friend.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. Johnny said to his mother, “I don’t know how to do this exercise.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
4. “We are waing for the school bus”, said the children.
__________________________________________________________________________________
5. Mary said, “My father died a year ago”.
__________________________________________________________________________________
6. John said, “I have nished studying my lesson”.
__________________________________________________________________________________
7. Mary said, “I cannot go to the movies with you, John”.
__________________________________________________________________________________
8. “I shall expect to see you next Wednesday.” Mary said to her friend.
__________________________________________________________________________________
9. He said, “I don’t know what happened.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
10. She said, “I went to the doctor yesterday.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
11. He said, “I have a toothache.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
12. She said, “I’ll write him a prescripon.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
13. They said, “We’re going to the drugstore.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
14. He said, “The doctor gave me some pills.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
15. She said, “I go to the supermarket every day.”
__________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 11. Read the text and answer the quesons.
Marie Curie
Marie Curie is the rst and only woman in the world to be honored twice with the Nobel Prize in two
dierent elds. She is regarded as the most outstanding female scienst in the world. It was Marie
Curie who found a way to ght cancer and X-ray technology...
During scienc research, Marie Curie and her husband discovered two important elements in the
periodic table: Polonium and Radium. This work paved the way for the advent of X-rays, which led to
many advances in medicine.
Today, advances have been made in X-ray technology allowing disease to be suspected, and radiaon
therapy is also used in the treatment of cancer.
Curie’s research has helped develop radiaon as a tool to treat cancer cells - the cornerstone of
radiaon therapy in modem medicine today, although radiaon therapy has improved. At that me,
she inserted small glass tubes with Radon (a radioacve gas) into areas of the tumor causing them to
shrink.
1. What are the two important elements in the periodic table discovered by Curie and her husband?
__________________________________________________________________________________
2. How are the advances made in X-ray technology used today?
__________________________________________________________________________________
3. How has Curie’s research helped develop radiaon?
__________________________________________________________________________________
4. Where on the human body did Curie insert small glass tubes containing Radon?
__________________________________________________________________________________
5. What is Marie Curie famous for?
__________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 12. Read and decide T (true) or F (false) for each statement.
Today our bookshop would like to introduce you a new book wrien by J.H. James. The book’s tle is
“Future world”. It is all about how new technologies will change our world in 2050. According to the
book, the an-aging drugs will help human live healthy lives over 120 years old. Another advanced
technology in health care is 3D prinng of human organs and body parts. This will be a good news to
diabetes paents because new muscles, bones and even organs will be rebuilt and replace the
damaged ones. About the technologies in environment protecon, solar power will be the main
energy source of the world in 2050. Solar panel will be more popular and help us reduce a large
amount of carbon dioxide emission. In addion, a new method of sewage treatment will solve
problems of water polluon. Industrial sewage will be treated to become clean water and minerals.
There is also some new advanced technology in transportaon. Cruise control will reduce the
accidents. This device will be very helpful especially for drunk drivers. In the future, a transponder will
also be installed in a bicycle and will reduce the crash. Read the book now and we can see that many
advanced technologies will bring us a safer and more convenient life.
Statement
T or F
1. “Future world” is the tle of the book which is introduced at the bookshop.
2. 3D prinng of human organs will help diabetes paents to build new organs and
body parts.
3. It is wrien in the book that in 2050, we will primarily use the energy generated
from the Sun.
4. According to the book, in the future, sewage will be treated by the same method
as present.
5. The author menons cruise control as a device which help to cut down the
accidents.
6. New advanced technology in transportaon isn’t wrien in the book.
Exercise 13. Read the text and ll in the blank.
Bicycles
The bicycle is one of the simplest yet most useful invenons in the world. What is most surprising is
that it was not (1) ______________ earlier, although the great inventor Leonardo da Vinci had drawn
pictures for bicycles and also for ying machines and some other things. Those things were not
produced (2) ______________ long aer he died.
A person riding a bicycle use (3) ______________ energy to make the bicycle move, and there is no
polluon at all when you are riding. Even so in developed (4) ______________, most people don't
travel to work by bicycle. It is not because the bicycles are expensive or people feel (5)
______________ if they ride to work. It's because (6) ______________ cars on the roads becomes
larger. It certainly becomes (7) ______________ to ride a bicycle. As a result, more people put their
bicycles away and go to work (8) ______________ their cars, and in this way, the situaon is made
more serious. (9) ______________ the best way to make riding safer and more popular is to create
paths only for bicycle and to make (10) ______________ so dicult and expensive for drivers to take
their cars into the city that they will go back to use their bicycles.
1. A. had
B. used
C. invented
D. ridden
2. A. before
B. when
C. since
D. unl
3. A. much
B. quite a lot of
C. very lile
D. many
4. A. world
B. countries
C. land
D. earth
5. A. lucky
B. glad
C. sorry
D. red
6. A. the number of
B. a number of
C. this kind of
D. all kinds of
7. A. safe
B. more dangerous
C. much
D. popular
8. A. by
B. in
C. use
D. drive
9. A. Hardly
B. Maybe
C. Perhaps
D. Nearly
10. A. it
B. them
C. us
D. that
Exercise 14. Turn these sentences into reported speech.
1. Paul said “I must go home now.”
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. “There’s been an accident and the road is blocked”, said the policeman.
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. “We are waing for the school bus”, said the children.
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. Mary said, “My father died a year ago.”
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. “Must you go now?”, said Mr. Brown.
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. “Whose bicycle did you borrow yesterday?”, his mother asked him.
___________________________________________________________________________________
7. “It isn’t so foggy today as it was yesterday”, said the teacher.
___________________________________________________________________________________
8. “Be modest if you are a good pupil”, said my father.
___________________________________________________________________________________

9. “Shut the door but don’t lock it”, she said to us.
___________________________________________________________________________________
10. Tom said, “New York is bigger than London.”
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 15. Turn the sentences below into direct speech.
1. My mother told me that she was sad then.
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. One of my friends said that she liked learning English with her teacher.
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. The doctor told me that I could leave the hospital that day.
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. The lm director said that she was willing to work then.
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. The teacher told his students that he would be busy the following month.
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. Tom invited me to his birthday party.
___________________________________________________________________________________
7. She said the doctor had wrien her a prescripon.
___________________________________________________________________________________
8. He said that he had a toothache.
___________________________________________________________________________________
9. She said she went to the museum every day.
___________________________________________________________________________________
10. They said they were going to the supermarket.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 16a. Read about the posive eects of science and technology in life. Then put the
headings into the correct posion.
Posive Eects:
Improved Communicaon
Medical Advancements
Convenience and Eciency
Globalizaon and Trade

Environmental Sustainability
Access to Informaon
Space Exploraon
1. _______________________________: Advancements in technology have enabled faster and more
ecient communicaon through the internet, smartphones, and social media, connecng people
across the globe.
2. _______________________________: Science and technology have led to breakthroughs in
medical research, leading to the development of new treatments, medicaons, and medical
procedures that have saved countless lives.
3. _______________________________: Modern technology has made tasks easier and more
ecient, from automated manufacturing processes to everyday tasks like cooking and cleaning.
4. _______________________________: The internet and digital libraries provide easy access to a
vast amount of informaon and educaonal resources, democrazing knowledge.
5. _______________________________: Science and technology have contributed to the
development of renewable energy sources and eco-friendly technologies aimed at reducing
environmental impact.
6. ____________________________________: Advances in transportaon and communicaon have
facilitated global trade and cultural exchange, beneng economies and sociees worldwide.
7. ____________________________________: Technological advancements have allowed humans to
explore space, leading to new scienc discoveries and potenal insights into the origins of our
universe.
Exercise 16 b. Read about the negave eects of science and technology in life. Then put the
headings into the correct posion.
Negave Eects:
Environmental Impact
Environmental Impact
Job Displacement
Job Displacement
Social Isolaon
Social Isolaon
Health Impacts
Increased reliance on technology for communicaon can lead to reduced face-to-face interacons
and a sense of isolaon.
1. _______________________________: The digital age has raised concerns about the misuse of
personal data, leading to issues of privacy and security breaches.
2. _______________________________: Automaon and Al have the potenal to replace certain
jobs, leading to unemployment and the need for reskilling in certain industries.
3. _______________________________: Prolonged screen me and sedentary lifestyles associated
with technology use can contribute to health issues like obesity, eye strain, and sleep disorders.
4. _______________________________: While technology can be used to promote sustainability, it
can also contribute to environmental degradaon through increased energy consumpon and
electronic waste.
5. _______________________________: Excessive use of technology can lead to addicon, aecng
mental and emoonal well-being and causing disrupons in personal relaonships.
6. _______________________________: The rapid pace of technological advancement can
somemes outstrip the development of ethical frameworks, leading to challenges in areas like Al
ethics, genec engineering, and more.
Exercise 17. Write a paragraph about the negave eects of science and technology in life.
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm
UNIT 12. LIFE ON OTHER PLANETS
A. VOCABULARY
WORD
PRONNCIATION
MEANING
alien (n)
/ˈeɪliən/
người ngoài hành nh
E.g. A few people found evidence of aliens on Earth. Một vài người m thấy bằng chứng về người
ngoài hành nh trên Trái đất.
commander (n)
/kəˈmɑːndər/
người chỉ huy, người cầm đầu
E.g. The commander rallied his troops around him. Người chỉ huy tập hợp quân đội xung quanh anh
ta.
crater (n)
/ˈkreɪtər/
miệng núi lửa
E.g. Ash began to erupt from the crater. Tro bụi bắt đầu phun ra từ miệng núi lửa.
creature (n)
/ˈkriːtʃər/
sinh vật, loài vật
E.g. Snail is a small plant-eang creature with a so body. Ốc sên là loài sinh vật ăn thực vật nhỏ, có
thân mềm.
galaxy (n)
/ˈɡæləksi/
thiên hà
E.g. Sciensts observing phenomena in nearby galaxies. Các nhà khoa học quan sát hiện tượng ở
các thiên hà lân cận.
gravity (n)
/ˈɡrævə/
trọng lực, lực hút trái đất
E.g. An apple falls down because of gravity. Một quả táo rơi xuống do trọng lực.
habitable (adj)
/ˈhæbɪtəbl/
có thể ở được, phù hợp để ở
E.g. This area is no longer habitable. Khu vực này không còn có thể sinh sổng được nữa.
Jupiter (n)
/ˈdʒuːpɪtər/
sao Mộc, Mộc nh
E.g. Jupiter is the largest planet in the Solar system. Sao Mộc là hành nh lớn nhất trong hệ Mặt
trời.
Mars (n)
/mɑːrz/
sao Hỏa, Hỏa nh
E.g. Is there life on Mars? Có sự sống trên sao Hỏa hay không?
Mercury (n)
/ˈmɜːrkjəri/
sao Thủy, Thủy nh
E.g. Mercury is the smallest of all the planets. Sao Thủy là hành nh nhỏ nhất trong tất cả các hành
nh.
Neptune (n)
/ˈneptjuːn/
sao Hải Vương, Hải Vương nh
E.g. Neptune is the furthest planet from the Sun. Sao Hải Vương là hành nh xa nhất từ Mặt trời.
oppose (v)
/əˈpəʊz/
chiến đấu, đánh lại ai
E.g. The children strongly opposed the idea. Những đứa trẻ phản đối mạnh mẽ ý tưởng này.
possibility (n)
/ˌpɒsəˈbɪlə/
khả năng, sự có thể
E.g. Bankruptcy is a real possibility if sales don’t improve. Phá sản là một khả năng có thế xảy ra nếu
doanh số bán hàng không được cải thiện.
promising (adj)
/ˈprɒmɪsɪŋ/
đầy hứa hẹn, nhiều triển vọng
E.g. The research produced promising results. Nghiên cứu tạo ra kết quả đầy hứa hẹn.
rocket (n)
/ˈrɒkɪt/
tàu vũ trụ con thoi
E.g. They launched a rocket to Venus. Họ đã phóng một tên lửa tới sao Kim.
Saturn (n)
/ˈsætɜːrn/
sao Thổ, Thổ nh
E.g. Saturn is the slowest mover of all the planets. Sao Thổ là hành nh chuyển động chậm nhất
trong tất cả các hành nh.
telescope (n)
/ˈtelɪskəʊp/
kính thiên văn
E.g. We can look at the stars through a telescope. Chúng ta có thể nhìn các vì sao qua kính thiên
văn.
trace (n)
/treɪs/
dấu vết, vết ch, dấu hiệu
E.g. He seems to have vanished without trace. Anh ta dường như đã biến mất không dấu vết.
UFO (n)
/ˌjuː ef ˈəʊ/
vật thể bay không xác định
E.g. I didn't believe reports of UFO sighngs. Tôi không n vào các báo cáo về việc nhìn thấy UFO.
Uranus (n)
/ˈjʊərənəs/
sao Thiên Vưong, Thiên Vưong nh
E.g. Uranus is unusual because it is lted. Sao Thiên Vương khác thường vì nó bị nghiêng.
Venus (n)
/ˈviːnəs/
sao Kim, Kim nh
E.g. Venus is of the same size as Earth. Sao Kim có cùng kích thước với Trái đất.
B. WORD FORMATION
Word
Related words
Transcripon
Meaning
adventure (n)
/ədˈventʃər/
cuộc phiêu lưu
adventurous (adj)
/ədˈventʃərəs
thích phiêu lưu, thích mạo hiểm
adventurously
(adv)
/ədˈventʃərəsli/
liều lĩnh, mạo hiểm
adventurism (n)
/ədˈventʃərɪzəm/
chủ nghĩa phiêu lưu
danger (n)
/ˈdeɪndʒər/
hiểm hoạ, mối đe doạ
dangerous (adj)
/ˈdeɪndʒərəs/
nguy hiểm
dangerously (adv)
/ˈdeɪndʒərəsli/
nguy hiểm, hiểm nghèo
poisonous (adj)
/ˈpɔɪzənəs/
độc, có độc
poison (n,v)
/ˈpɔɪzn /
chất độc, thuốc độc, đầu độc
terrorist (n)
/ˈterərɪst/
kẻ khủng bố
terrorize (v)
/ˈterəraɪz/
làm cho khiếp sợ, khủng bố
terrorism (n)
/ˈterərɪzəm/
sự khủng bố, chính sách khủng bố
weightless (adj)
/ˈweɪtləs/
không trọng lượng
weight (n)
/weɪt/
trọng lượng
weightlessness (n)
/ˈweɪtləsnəs
trạng thái không trọng lượng
C. GRAMMAR
1. Reported speed (quesons) - Lòi nói gián ếp (câu nghi vấn)
Khi chuyển câu hỏi trực ếp thành giản ếp cũng cần áp dụng quy tắc chuyển đổi 3 bước giong như
câu trần thuật.
Bước 1: Đổi ngôi
Bước 2: Lùi thì
Bước 3: Chuyển các cụm từ chỉ thời gian, noi chốn
Tuy nhiên trong câu hỏi có một số thay đổi sau:
- Động từ tường thuật câu hỏi gián ếp là asked/ wanted to know/ wondered...
- Trật tự từ chuyển về dạng trần thuật tức là chủ ngữ đứng trước động từ, câu không còn đảo ngữ
nữa.
- Không dùng liên từ “that’, dấu được bỏ đi.
a. Yes/no quesons:
S + asked + (O) + if / whether + clause (S’ + V
lùi thì
)
E.g. Tuan asked Ba “Are you fond of watching television?”
Tuan asked Ba if/whether he was fond of watching television.
E.g. “Do you like listening to music?” she asked me.
She asked me if I liked listening to music.
b. Wh-quesons:
S + asked + (O) + wh - word + clause (S’ + V
lùi thì
)
E.g. He said to me, “Why did you go with her mother last week?”
He asked me why I had gone with her mother the week before.
E.g. “Where did you go last night?”, her mother asked.
Her mother wanted to know where she had gone the night before.
Chú ý: Trong trường hợp câu trực ếp có cả câu trần thuật và câu hỏi khi đổi sang câu gián ếp dạng
câu nào sẽ đổi theo quy tắc dạng câu đó.
E.g. “I have le my watch at home. Can you tell me the me?”
He said that he had le his watch at home and asked me if I could tell him the me.
D. PRONUNCIATION
Intonaon for making lists - Ngữ điệu trong câu liệt kê
Trong câu liệt kê, ngữ điệu sẽ lên cao ở những từ đầu và xuống thấp vào từ cuối để chỉ ra rằng danh sách hoặc
sự liệt kê đã kết thúc.
E.g. We like playing football , basketball , volleyball and tennis .
(Chúng tôi thích chơi bóng đá, bóng rổ, bóng chuyền và quần vợt.)
E.g. I le work , came home , took a shower , had dinner , watched TV , and went to bed .
(Tôi tan làm, trở về nhà, đi tắm, ăn tối, xem phim và đi ngủ.)
E. PRACTICE
Exercise 1. Single-underline the words that have high intonaon and double-underline the words
that have low intonaon in the following sentences.
1. There are 8 planets in the solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and
Neptune.
2. Do you like tea, coee or lemonade?
3. Five oceans in the world including the Pacic Ocean, the Atlanc Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the
Arcc Ocean and the Southern Ocean.
4. Is your father coming today or tomorrow?
5. Which color palee do you prefer? The shades of green or blue?

6. The 7 colors of the rainbow are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and purple.
Exercise 2. Read the sentences in exercise 1 aloud and emphasize the underlined words with correct
intonaon.
Exercise 3. Complete the sentences with the words or phrases in the box.
planet
traces
Solar system
weightless
ying saucer
space buggy
galaxy
aliens
outer space
astronaut
1. A _______________ is somemes referred to as an Unidened Flying Object (UFO).
2. An _______________ is a person who is trained for travelling in a spacecra.
3. Researchers made the amazing ndings of _______________ of water on Mars.
4. A _______________ is a vehicle used for driving on the Moon.
5. Our _______________ is made up of the Sun and all the objects that travel around it.
6. Earth is the only _______________ known to be habitable.
7. Do you believe _______________ exist on other planets?
8. Spacecra are vehicles used for travel in _______________.
9. Our _______________, the Milky Way, consists of 100 - 400 billion stars.
10. Astronauts on the orbing space staon are _______________ because they do not experience a
force of gravity.
Exercise 4. Choose the correct answers to complete the sentences.
1. _______________ is the name of a planet that matches the Roman God of the sea.
A. Mars B. Sun C. Venus D. Neptune
2. Discovered in the Kuiper belt beyond Neptune, _______________ is a dwarf planet.
A. Jupiter B. Pluto C. Saturn D. Mercury
3. Unidened Flying Objects or “_______________” haven’t been formally recognized.
A. UFOs B. spaceships C. space shules D. spacecra
4. Some people believe the _______________ was created by a big explosion.
A. galaxy B. atmosphere C. universe D. outer space
5. _______________ is named aer the Roman God of war.
A. Uranus B. Jupiter C. Mars D. Venus
6. A(n) _______________ is a scienst who studies the stars and planets.
A. captain B. alien C. astronaut D. astronomer
7. Astronauts _______________ around in space because there is no gravity in space.
A. y B. oat C. walk D. trace
8. In a weightless environment, everything oats _______________.
A. uncontrollably B. downwards C. smoothly D. constantly
9. On June 2
nd
, 1966, Surveyor 1 became the rst U.S. _______________ to land on the moon.
A. ying saucer B. airplane C. spacecra D. helicopter
10. Mars is the most _______________ planet in our Solar System besides Earth.
A. powerful B. notable C. appropriate D. habitable
Exercise 5. Circle the correct answers.
1. Interviewing applicants for an important job can be a very me-_______________ process but it’s
worth in the end.
A. lasng B. developing C. consuming D. taking
2. Before you start applying for any job, you must be absolutely sure you have the right paper
_______________.
A. qualies B. qualiers C. qualifying D. qualicaons
3. His invenon showed that he understood what was going to happen in the future and proved he
was _______________ of his me.
A. in front B. before C. ahead D. forward
4. You have a cket to the game, _______________?
A. do you B. haven’t you C. don’t you D. have you
5. Kumar asked me a queson but I don’t know what _______________.
A. is the answer B. was the answer C. the answer is D. the answer was
Exercise 6. Circle the correct answers.
1. Tourist: “Where is the post oce?”
→ A tourist asked me where _______________.
A. the post oce has B. the post oce was
C. is the post oce D. was the post oce
2. Mom: “It’s 2 a.m.; what are you doing in the kitchen?”
→ Mom wanted to know what _______________ in.
A. was I doing B. I do C. I was doing D. am I doing
3. Dad: “Why did you come home so late last night?”
→ Dad wanted to know _______________ home very late the night before.
A. why did I come B. if I come C. if I came D. why I had come
4. Jane: “Have you ever been to Australia?”
→ Jane asked me _______________ to Australia.
A. if I’m ever going B. if I’d ever been C. have I ever been D. had I ever been
5. Joe: “Could you sing when you were ve?”
→ He asked me _______________ when I was ve.
A. can I sing B. if I can sing C. could I sing D. if I could sing
6. Mother: “When are you going to do your homework?”
→ Mother asked me when _______________ to do my homework.
A. was I going B. I was going C. am I going D. I’ll be going
7. Allen: “How many songs had John Lennon wrien before he died?”
→ Allen wanted to know how many songs _______________ before his death.
A. John Lennon had wrien B. John Lennon was wring
C. was John Lennon wring D. had John Lennon wrien
8. Janet: “Were you working at 8 p.m. last night?”
→ Janet asked me _______________ at 8 p.m. the other night.
A. if I’m working B. if I’d been working
C. was I working D. had I been working
9. Dad: “Have you been aending classes regularly?”
→ Dad asked me _______________ aending classes regularly.
A. if I’d be B. had I been C. if I’d been D. have I been
10. Mario: “What should I do to improve my English?”
→ Mario asked his teacher what _______________ to improve his English.
A. he should do B. he would do C. shall he do D. should he do
11. Jim: “How much does your sister earn?”
→ Jim wanted to know how much _______________.
A. my sister has earned B. did my sister earn
C. does my sister earn D. my sister earned
12. Joe: “Could you sing when you were ve?”
→ He asked me _______________ when I was ve.
A. can I sing B. if I can sing C. could I sing D. if I could sing
13. Mary: “Are you able to swim?”
→ Mary asked me _______________ to swim.
A. if I have been able B. am I able
C. if I was able D. will be able
14. Tourist: “When was that castle built?”
→ The tourist asked the guide when _______________.
A. had the castle built B. the castle had been built
C. the castle was being built D. was the castle built
15. Sue: “May I sleep at Lee’s house overnight?”
→ Sue asked her mother _______________ at her friend’s house overnight.
A. if she might sleep B. could she sleep C. can she sleep D. if she had to sleep
Exercise 7. Turn these sentences into reported speech.
1. “Where is my umbrella?” she asked.
→ She asked
2. “How do you learn English?” Marn asked us.
→ Marn asked us
3. He asked, “Do I have to do it?”.
→ He asked
4. “Where have you been?” the mother asked her daughter.
→ The mother asked her daughter
5. “Which dress do you like best?” she asked her boyfriend.
→ She asked her boyfriend
6. “What are they doing?” she asked.
→ She wanted to know
7. “Are you going to the cinema?” he asked me.
→ He wanted to know
8. The teacher asked, “Who speaks English?”
→ The teacher wanted to know
9. “How do you know that?” she asked me.
→ She asked me
10. “Where did you meet her?” my friend asked me.
→ My friend asked me
Exercise 8. Turn these sentences into reported speech.
1. “Do you speak English?” he asked me.
→ He asked me
2. “Are you Brish or American?” she asked me.
→ She asked me
3. “Have you got a computer?” she asked.
→ She wanted to know
4. “Can you type?” he wanted to know.
→ He asked
5. “Did you come by train?” she wanted to know.
→ She wanted to know
6. “Have you been to Bristol before?” he asked.
→ He asked
7. “Will you be at the party?” he asked her.
→ He asked her
8. “Can you meet me at the staon?” she asked me.
→ She asked me
9. “Did you see that car?” he asked me.
→ He asked me
10. “Have you died up your room?” the mother asked the twins.
→ The mother asked the twins
Exercise 9. Choose the correct opon to complete each sentence.
1. She asked me where I _______________ from.
A. come B. coming C. to come D. came
2. She _______________ me whether I liked classical music or not.
A. ask B. asks C. asked D. asking
3. He asked me who _______________ the editor of that book.
A. was B. were C. is D. has been
4. He wants to know whether I _______________ back tomorrow.
A. come B. came C. will come D. would come
5. I wonder why he _______________ love his family.
A. doesn’t B. don’t C. didn’t D. hasn’t
6. They asked me how many children _______________.
A. if I had B. had l C. I have D. have I
7. Thu said she had been _______________ the day before.
A. here B. there C. in this place D. where
8. The student said that the English test _______________ the most dicult.
A. is B. was C. will be D. have been
9. He wanted to know _______________ shopping during the previous morning.
A. if we had been going B. that if we had been going
C. we were going D. that we were going
10. He asked me _______________ Robert and I said I did not know _______________.
A. that did I know / who were he B. that I knew / who he had been
C. if I knew/ who he was D. whether I knew / who had he been
11. They said that they had been driving through the desert _______________.
A. the previous day B. yesterday C. the last day D. Sunday previously
12. He asked the children _______________ too much noise.
A. not to make B. not making C. don’t make D. if they don’t make
13. The man said that money _______________ the passport to everything.
A. will be B. is C. was D. can be
14. The teacher said Columbus _______________ America in 1942.
A. discovered B. had discovered C. was discovering D. would discover
15. John said he _______________ her since they _______________ school.
A. hasn’t met - le B. hadn’t met - had le
C. hadn’t met le D. didn’t meet – has le
16. The woman asked get lunch at school.
A. can the children B. whether the children could
C. if the children can D. could the children
17. Laura said that when she _______________ to school, she saw an accident.
A. was walking B. has walked C. had been walking D. has been walking
18. He asked, “Why didn’t she take the nal exam?” - He asked why _______________ the nal exam.
A. she took B. did she take C. she hadn’t taken D. she had taken
19. Ba said he _______________ some good marks the semester before.
A. gets B. got C. had goen D. have got
20. They told their parents that they _______________ their best to do the test.
A. try B. will try C. are trying D. would try
Exercise 10. Read the passage and answer the following quesons.
MERCURY
Among eight planets in our Solar system, Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun and it needs only 88
days to complete an orbit around the Sun. According to Greek mythology, Mercury is the messenger
of Gods (Hermes). Mercury is a small planer that bears a strong resemblance to the Moon with its
lile larger size rocky surface and many bowl-shaped cavies. Because of its posion in the Solar
system, the temperature on the sunny side of Mercury can reach over 800 degrees but -300 degrees
is the other side’s temperature. Being cooler than only Venus, the hoest planet, the climate on
Mercury is extremely severe which makes it hard to visit and explore. Two spacecra have been sent
to Mercury, the rst was in 1974 and sciensts had to wait three decades to visit Mercury the second
me in 2004. Some people believe that there is no water in Mercury but some informaon collected
from Radar showed that ice exists on the Northern pole of this planet. Small Mercury has no moons
and no atmosphere because of its too lile gravity (38% of the gravity of Earth). There is no report
showing life's existence in Mercury yet.
1. How long does it take Mercury to orbit the Sun?
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. In Greek mythology, who is the messenger of Gods?
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. According to the passage, why is Mercury similar to the Moon?
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. What is the highest temperature on Mercury?
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. How many spacecra have been sent to Mercury?
___________________________________________________________________________________
Exercise 11. Read the passage carefully then answer the quesons.
How many planets are there in our galaxy? That’s a tricky queson to answer. Are there other planets
that support life? That’s exactly what the Kepler mission hopes to discover.
NASA launched the Kepler space telescope, designed to nd habitable planets, in 2009. So far it has
discovered ve new Earth-sized planets beyond our Solar System. These planets are hoer than the
Earth - much too hot for life as we know it. The Kepler team predict that they will need at least three
years to nd an Earth-like planet.
The simplest requirement for a planet to have life is for there to be liquid water so the distance from
the planet’s sun and therefore temperature is important. There also needs to be the correct amount
of air. If a planet is as small as Mars (half the size of Earth) its weak gravity means that it can’t hold on
to air molecules. If a planet is Neptune-sized (four mes bigger than Earth) it has very strong gravity
and too much air. So size maers too.
The cost of the mission is approximately six hundred million dollars. It is scheduled to observe unl
2013 but this could be extended. Will we be sad if we discover we are alone in our galaxy or happy if
we nd that we share it with other life forms?
1. What is the passage about?
A. Planets in our Solar System
B. The dierence between Earth and other planets
C. Space exploraon to nd habitable planets
D. NASA’s missions to explore the outer planets
2. The Kepler space telescope is looking for.
A. new planets in our galaxy B. life on other planets
C. liquid water on other planets D. Earth-sized planets in the Solar System
3. Kepler has found ve planets that.
A. has water and air B. are similar to Earth
C. are not too far away from the Earth D. are not in our Solar System
4. The Kepler team predict that they will need to nd an Earth-like planet.
A. three years and possibly longer B. as much as three years
C. no more than three years D. approximately three years
5. What are the primary factors that make a planet habitable?
A. Liquid water and living things B. Size and distance from the Sun
C. Hot temperature and weak gravity D. Strong gravity and too much air
6. How much does the Kepler mission cost?
A. Exactly $600 million B. About $600 million
C. More than $600 million D. Less than $600 million
7. Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A. The planet can support life if it has water and air.
B. A very small planet will not have enough air.
C. Earth is four mes as big as Neptune.
D. Kepler mission is scheduled to end in 2013.
Exercise 12. Turn the sentences into reported speech. (Yes/ no quesons.)
1. “May I ask you a few quesons?”
→ The woman asked John
2. “Have you done your project about space exploraon?”
→ The teacher asked me
3. “Will we be able to live on Mars in 2050?”
→ Debbie asked her father
4. “Are you having a barbecue tonight?”
→ I asked the Browns
5. “Do you like sci- lms that feature extraterrestrial life?”
→ Jane asked Tom
6. “Did sciensts nd life on Mars many years ago?”
→ Vai asked me
7. “Are aliens or UFOs real?”
→ Many people wondered
8. “Can we go to the Naonal Museum tomorrow?”
→ Sally asked her best friend
9. “Do you know NASA has found two new planets?”
→ Due asked Trang
10. “Were you here yesterday?”
→ She wanted to know
Exercise 13. Turn the sentences into reported speech. (Wh-quesons.)
1. “Where will we live in 20 years’ me?”
→ Jane asked me
2. “How was your trip to Toronto?”
→ I asked Peter
3. “Why didn’t Judy wait for reballs last night?”
→ Sue asked
4. “How many planets are there in the solar System?”
→ The teacher asked us
5. “How many days does it take to get to Mars from Earth?”
→ Elliot wanted to know
6. “What are you staring at?”
→ I asked Sally
7. “Who discovered the planet Neptune?”
→ Joe asked his teacher
8. “How long have you been living on the Internaonal Space Staon?”
→ He asked the astronaut
9. “When will humans go to Venus?”
→ The students wanted to know
10. “Where are you going this summer holiday?”
→ I asked Sally and Andy
Exercise 14. Rewrite the sentences without changing the meaning of the original sentences.
1. Reading scienc books is one of my interests.
→ I’m
2. Unless he phones her immediately, he won’t get any informaon.
→ If
3. The garage is going to repair the car for us next week.
→ We are going to
4. The news was so wonderful that she decided to have a celebraon.
→ It was
5. It’s very dicult to leave here aer such a long me.
→ It isn’t
6. I always see him working in the garden on Sundays.
→ He takes
7. 18 people came although we had expected only 16.
→ Two extra
8. Jerry’s salary as an accountant is two thousand dollars a month.
→ Jerry makes
9. We need a week to think about it.
→ We need
10. The owners of newspapers are usually very rich.
→ The people
Exercise 15. Change the sentence from direct speech to indirect speech.
1. Mr. Smith said to me: “Where are you going on your vacaon this year?”
→ Mr. Smith asked me
2. She said: “Did the mechanics nish repairing your car?”
→ She asked
3. She said: “Why has David been looking so miserable lately?
→ She wanted to know
4. I asked my friend: “Did you have a car accident last month?”
→ I asked my friend
5. She asked me: “How old are you now?”
→ She asked me
6. He said to her: “Have you been to the town today?”
→ He asked her
7. John said: “How long does it take you to get to London, Mary?”
→ John asked Mary
8. The policeman asked the lile girl: “What’s your name?”
→ The policeman asked the lile girl
9. Mr. Green said to his secretary: “Who did you talk to a few minutes ago?”
→ Mr. Green asked his secretary
10. Paul said: “Can you swim, Mary?”
→ Paul asked Mary
11. He said: “Where can I nd her in this town?”
→ He asked
12. She asked her son: “Do you know this story?”
→ She asked her son
Exercise 16. Change the sentence from indirect speech to direct speech.
1. He asked where his phone was.
___________________________________________________________________________________
2. He wanted to know what I was doing.
___________________________________________________________________________________
3. My sister asked me if Emily had talked to Jessica.
___________________________________________________________________________________
4. She wanted to know if I was going to bed.
___________________________________________________________________________________
5. He asked me if I had locked the door.
___________________________________________________________________________________
6. She said she could play the guitar when she was seven.
___________________________________________________________________________________
7. He said that he didn’t like peanut buer.
___________________________________________________________________________________
8. Lily said that I should go to school early.
___________________________________________________________________________________
9. Becky asked me to help her.
___________________________________________________________________________________
10. The music teacher told us not to play the guitar in that room.
___________________________________________________________________________________
Giaoandethitienganh.info sưu tầm